The fundamental problem with “network neutrality” rules aptly is illustrated by Apple’s talks with Comcast about enabling an Apple set-top box that has assured quality of service on Comcast’s high speed access network.
In other words, Apple does not want “best effort access,” which is what network neutrality mandates. Instead, Apple wants a managed service with quality of service controls.
Some immediately will note that what Apple wants is not "packet prioritization" of the type forbidden by network neutrality rules.
But some will say the nomenclature is a bit of a ruse.
To wit, Apple does not believe “best effort” is good enough to ensure the quality of its proposed streamed content, and wants to be provided as a managed service over Comcast's access network.
To be sure, the Federal Communications Commission specifically exempts such managed services from the network neutrality rules.
But some will note the irony: an IP app a "managed service" is lawful. An over the top Internet app cannot use priority delivery mechanisms.
If Apple succeeds, you can be sure a wave of new "managed services" will be created, using prioritized access.
One immediate question is what is required for a service to be considered a "managed service," not an over the top Internet app. On the face of it, it would seem to be the offering of such a service by an Internet service provider directly, much as telcos, cable companies and satellite providers sell "managed" voice service or linear video entertainment.
In other words, "who owns the service" might well become the clear delineation.
That also suggests lots of opportunity for future business deals between over the top and ISP partners to create such managed services. In large part, that would render "network neutrality" a bit more hollow.
Such "who owns the service" regulation is one reason many have supported “network neutrality;The whole point of such a framework was to prevent ISPs from favoring "their own" apps over similar offerings provided by independent third parties.
The potential Apple deal with Comcast would increase the uncertainty about the soundness of the framework long term.
Few would question, at least at this point, the "right" of a facilities-based access service provider to create its own branded managed services.
That is what voice service is, after all.
Likewise, nobody would question the right of a TV or radio broadcaster, telco, cable company or satellite services provider to create and deliver a service over its own network.
The big issue has been the framework for over the top, unaffiliated apps and services.
The Apple proposal gets around that issue because the proposed streaming service essentially would be a service created and "owned" by the access provider (even if Apple is the essential partner).
There are some trade-offs for the video service supplier. It might mean such a managed service is not available as an Internet app, only as a for-fee service offered by one or more ISPs.
That will limit potential audience to a certain extent, unless the managed service reaches agreement with most of the ISPs in a market that represent 80 percent to 90 percent of the potential customer base.
The enduring issue is that quality delivery of paid-for video entertainment is subject to the same congestion issues that cause video stalling as all other apps when access networks are congested.
In seeking to become a managed service, Apple wants priority delivery of its video bit, the very sort of thing network neutrality advocates have opposed.
But that is the fundamental problem with network neutrality, some would argue. Prioritized access, under conditions of congestion, is a surefire way to deliver the bits with higher end user value.
Consumer welfare, in other words, is increased when consumers get priority delivery of apps that are highly susceptible to degradation when access networks are congested.
Apple’s efforts essentially are a rebuke to the notion that network neutrality actually enhances consumer welfare.
It is one thing to argue that all lawful apps should be accessible to any user of the Internet. Everybody agrees on that point.
The Federal Communications Commission, furthermore, already has adopted “no blocking” as a fundamental principle.
But priority delivery is not blocking. It is a mechanism for providing quality of service when networks are congested. It’s the same principle as all content delivery networks lawfully use.
Apple wants its video streaming traffic managed, not delivered “best effort,” as is Comcast Internet traffic; in other words, to have its service offered as a managed service, not an “Internet app,” as Comcast’s linear TV also is treated.
Precisely how regulators might view any future service of this type is not clear.
The FCC already exempts “managed” services from the “best effort only” network neutrality principle.
The important observation is that Apple is pointing out why prioritized access (even when it is called something else) is so important for voice and video apps, and why “best effort only” is not an optimal solution for delivering applications highly dependent on stable and predictable bandwidth.
Monday, March 24, 2014
Apple Wants Priority-Assured Video Services Delivery
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Sunday, March 23, 2014
Why "Cloud" is Strategic for Capacity Providers
“Cloud” is a key business concept and the underpinning of revenue growth strategy for capacity providers, not simply a new computing architecture for app providers.
Simply, revenue growth hinges largely on serving the needs of content providers and data centers serving content providers. Content demand now drives the places bandwidth has to be supplied, why it has to be supplied, and therefore where transport revenues can be earned.
And those are some of the ways “cloud computing” is shaping transport provider revenue opportunities.
Simply, revenue growth hinges largely on serving the needs of content providers and data centers serving content providers. Content demand now drives the places bandwidth has to be supplied, why it has to be supplied, and therefore where transport revenues can be earned.
Instead of networks optimized for moving symmetrical narrowband traffic from one telco point of presence to another telco point of presence, the long-haul networks now mostly move asymmetrical broadband traffic from one data center to other data centers.
That shift to “east-west” (server to server) traffic, from “north-south” (client to server) is shaping demand for capacity, and therefore revenue, with a big role played by end user demand for content, and hence for content delivery networks.
About 51 percent of all Internet traffic will cross content delivery networks in 2017 globally, up from 34 percent in 2012, according to Cisco. And since much of that content is high-bandwidth entertainment video, CDN-related traffic flows now are crucial for transport services providers.
The other big change wrought by cloud-based content apps is dramatic change in the geography of demand.
In fact, Cisco estimates, metro traffic volume will surpass long-haul traffic in 2014, for example, and will account for 58 percent of total IP traffic by 2017.
In fact, metro network traffic will grow nearly twice as fast as long-haul traffic from 2012 to 2017, Cisco argues. And much of that traffic will consist of video.
Globally, IP video traffic will be 73 percent of all IP traffic (both business and consumer) by 2017, up from 60 percent in 2012.
Cloud architecture has other implications for transport providers, namely the way cloud-based apps are “assembled,” rather than simply served up whole to requesting users. That is one reason why east-west traffic is growing.
Transport provider revenue growth increasingly is driven by supporting customers needing to move large amounts of content--especially video--from one data center to another, to assemble full apps or pages served up to end users.
In fact, the bulk of global undersea traffic arguably now consists of video-based Internet applications, hosted from huge data centers. One way of describing such east-west traffic flows is that traffic moves between servers, not between an end user and a server.
Though the actual application the end user uses is a communication north-south (client to server), often much of the “app” gets assembled from multiple servers.
And those are some of the ways “cloud computing” is shaping transport provider revenue opportunities.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Friday, March 21, 2014
Twitter Cutoff in Turkey is What Blocking Really Looks Like
Twitter was blocked in Turkey after Turkish Prime Minister Tayyip Erdoğan objected to tweets critical of his government. That is what app blocking really looks like.
Network neutrality, by way of comparison, concerns only the preservation of "best effort only" levels of Internet access by consumer customers.
Network interconnection, or Internet domain interconnections, which some want to drag into the network neutrality framework, also is not "blocking" of lawful apps.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
E-Commerce is a Winner Take All Market, So Far
Another example of “winner take all” economics in Internet-based content, e-commerce and advertising markets, where a few giant competitors rule the market.
Amazon is larger than the next dozen largest e-tailers combined. That same sort of effect can be seen in mobile advertising, over the top video entertainment, and is developing in over the top messaging.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Average U.S. Internet Access Speeds Double in 3 Years
Average U.S. Internet access speeds have doubled in just three years, according to Broadband for America.
IN 2010, the average connection speed in the United States was 4.7 Mbps. In the third quarter of 2013, the average connection speed had more than doubled to 9.8 Mbps. while the average peak connection speed was 37.0 Mbps.
Rapid increases, despite some sense, in some quarters, that change is not rapid enough, have been quite rapid, indeed, in large part because of retail offers from cable companies.
The standard cable broadband speed has increased 900 percent since 1999.
In August 2000, only 4.4 percent of U.S. households had a home broadband connection, while 41.5 percent of households had dial-up access.
A decade later, dial-up subscribers declined to 2.8 percent of households in 2010, and 68.2 percent of households subscribed to broadband service.
In other words, from 2000 to 2012, the typical purchased access connection grew by about two to three orders of magnitude in about a decade.
If that continues, gigabit connections will be common within two decades.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Do French and U.S. Mobile Markets Have Too Many Competitors?
Does the U.S and French mobile business have “too many” or “too few” contestants? And no matter which view is taken, on what basis are informed judgments made?
Consider the rival bids being made by Altice, owner of French cable concern Numericable, and Bouygues, a leading French mobile operator, for the assets of Vivendi’s SFR mobile business.
In the wake of a decision by SFR to negotiate exclusively with Altice, Bouygues had been expected to pursue a merger with Iliad, which owns France's fourth mobile operator, Free Mobile.
Observers say regulatory risk is an important element of SFR thinking. A Bouygues purchase of SFR would reduce the number of national mobile providers from four to three, while French regulators prefer a minimum of four providers.
In that view, a purchase of SFR by a cable company would be preferable to reducing the number of mobile service providers. Of course, some would argue the mobile segment currently has too many contestants for a stable, healthy, longer term market that remains competitive.
In the U.S. market, Sprint has been sounding out regulators about a potential bid by Sprint to acquire T-Mobile US. By all accounts, U.S. Federal Communications Commission and antitrust authorities at the Department of Justice are skeptical about such a potential merger.
The reasons fundamentally are the same as in France: regulators have more confidence in a four-player market than a three-provider market, in terms of maintaining robust competition.
The problem is that there is no way to know, in advance, which position--the market is too concentrated, or the opposite market is not concentrated enough--is correct, in terms of maintaining both robust competition and also incentives for continual investment.
In fact, globally, a “rule of three” already seems manifest. That is to say, in any mature industry, three suppliers dominate the market. Of 40 major markets studied by mobile analyst Chetan Sharma, the top three mobile operators controlled 93 percent of their respective markets.
In some “hyper-competitive markets” like the United Kingdom and the United States, “which had more than four to five large players” are moving towards the consolidation phase where the top three control more than 80 percent of the market, Sharma has said.
Opponents of a Sprint acquisition of T-Mobile US argue that consumer retail prices likely will rise, in the event of a merger. Indeed, that is one reason why most equity analysts think only such a merger will end the current price war in the U.S. mobile market.
Economists and analysts at the Phoenix Center for Advanced Legal and Economic Policy Studies agree that retail prices likely would rise in the wake of a Sprint acquisition of T-Mobile US, but also argue that isn’t the point. Even higher retail prices do not tell the long-term story about sustainable levels of robust competition and sustainable incentives for continued investment.
Though it sometimes seems counter-intuitive, retail prices that are too low necessarily drive weaker competitors out of the market, leading to more market concentration. Prices that are too low also dissuade contestants from investing aggressively, as there is little to no profit for doing so.
But the issue is whether any regulatory bodies, anywhere, are smart enough to know, in advance, whether consumer welfare outcomes are better with three or four national providers.
Economic theory suggests “excessive competition” can lead to negative profits, and therefore death, of all contestants in a market with too many competitors. Consolidation is the inevitable result.
And, one might well argue,, such consolidation provides a better outcome for consumers. 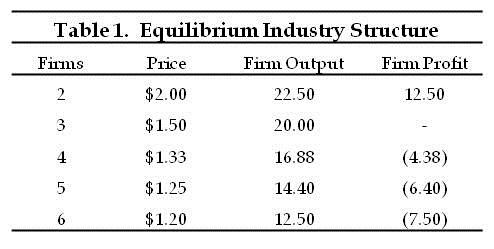
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Thursday, March 20, 2014
Winner Take All Markets Have Clear Business and Regulatory Implications
Some would point to modern retailing and the rise of Wal-Mart as one example of a winner take all market.
Many would say the music industry, and digital information or content businesses, increasingly take on a “winner take all” character. Some argue that is true in large part because information technology now allows any single firm to reach huge markets, affordably, compared to what was possible in the past.
That means the very best supplier in any industry affected by economies of scale--and that is most industries these days--will do disproportionately well.
Some might argue “winner take all” economics easily can arise in industries where fixed cost is high and marginal costs are low.
If that sounds familiar, it is because that is the structure of the global telecom business as well. “Winner take all” might be expressed as the “rule of three,” describing the typical national telecom market which is dominated by no more than three providers.
One example is the new concentration of revenue in the mobile advertising business.
For observers long accustomed to the relative fragmentation of advertising revenues and market share across television, radio, newspapers and magazines, the extreme concentration of mobile advertising revenue is shocking.
Facebook and Google accounted for about 67 percent of all global mobile ad market revenue in 2013, and it is projected that Facebook and Google will earn nearly 69 percent of all global mobile ad revenue in 2014.
Between them, Google and Facebook earned 75 percent of the $9.2 billion in incremental global mobile ad revenues in 2013 ($6.92 billion), according to eMarketer .
That's one example of a "winner take all" market. Of course, there are implications for regulators responsible for oversight of communications markets. To the extent the theory holds, only a few firms will dominate every telecom market, eventually.
That tendency to "fewness" will be relevant in coming days as much of the global communications business consolidates. The point is that, no matter what, a truly competitive market will eventually consolidate into leadership by just a few companies.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Demography is Why OTT Video Wins, in the End
| http://www.parksassociates.com/blog/article/pr-mar2014-ott-webcast |
The way younger users consume entertainment video tells you most of what you need to know about the inevitability of over the top, streamed video that competes directly with linear video subscriptions, even if, in an interim period, it might well turn out that linear video subscription providers emerge as key purveyors of such services.
In what linear video service providers might consider an ideal scenario, consumers would be able to stream only the shows and programs they want to watch, on demand, if they also purchase a linear video service that accompanies the over the top access, even if they do not want to watch linear video, or possibly even do not own televisions.
That is the direction major linear video suppliers already are headed, at least for the major television networks, essentially adding “on the go” access to some of the channels and content subscribers already pay for as part of their linear video subscriptions.
How successful such approaches might be in a future market is not so clear, but, in principle, many consumers might accept new packages supporting both on demand streamed access as well as linear TV access, if the retail pricing questions can be addressed.
In other words, many users will refuse to pay $100 or more for linear access, only to get streamed access as part of the package. Whether they might be willing to pay lower amounts, for smaller channel packages, plus streamed access, is not yet clear.
Of course, it never is easy to convince consumers they have to pay one product they don’t want, to get access to another product they do want. Requirements to buy fixed voice service in order to get high speed access provide one recent example of that sort of retail packaging.
Likewise, video service providers typically require consumers to buy basic cable first, in order to buy a premium channel such as HBO.
Movie services already are well down the path of mass adoption, by way of contrast, as consumers have grown accustomed first to renting videocassette tapes, then DVDs, and now streaming Netflix, Amazon Prime and other content.
Perhaps 45 percent to 50 percent of U.S. broadband households now use paid over-the-top (OTT) video services, either subscription or transactional, according to Parks Associates. That is up slightly over about a year’s time.
Including “free” sources such as YouTube, perhaps 70 percent of Internet users watch at least some over the top video.
Parks Associates also notes that 37 percent of consumers 18 to 24 view online video is their most important video source.
More than 40 percent of U.S. broadband households selected online video as one of the top three important sources of video, topping rental DVDs at 25 percent and 13 percent who said owned Blu-ray discs were among the top three sources.
The key observation is the huge difference in video entertainment preferences between the oldest and the youngest age cohorts, with roughly linear correlations in demand across all age cohorts, namely that the older the user, the less reliance is placed on over the top, streamed sources.
The younger the user, the more reliance is placed on streamed video entertainment. For users 34 or younger, online sources are at least as important as linear video, and among those younger than 24, the most-used delivery mode.
Should those behaviors persist as younger consumers grow older, linear video demand will drop, and content now delivered using linear retail formats will have to shift.
But there is one important observation about the timing of such a change. Though one might argue the transition will be about as linear as the consumption graph indicates, this almost certainly will not be the case.
When the disruption happens, and linear content is made available on a streamed basis, behavior will shift rapidly, in quantum fashion, not linearly. The reason for the prediction is simple: all other popular mass market services have shown a quantum, not linear adoption pattern.
Demography is destiny, one often hears, as a quip. But it is a quip with solid rooting. As Liberty Media CEO John Malone once quipped, in response to an analyst’s question about take rates for cable TV, specifically the fact that some consumers had high resistance to buying the product, Malone quipped that this was true, but “those people are dying.”
For it is a simple fact that generations of people eventually die, and are replaced by successive generations of people. So when researchers see significant generational demand for some products, the habits of the younger age cohorts are strategic, as they represent the future consumption patterns of virtually all age cohorts.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Ad-Supported Communications Takes Scale
Entrepreneurs have been trying to create advertising-supported communication services for decades, with no success. Recently, mobile service providers have been trying to do so in the United Kingdom.
Samba Mobile is one such effort.
Blyk was another U.K.-based effort. But Blyk shifted course to become an advertising services provider.
OVIVO, another mobile virtual network operator using the advertising model has shut down. The crowdsourced firm had raised £440,000 from crowdsourcing site Crowdcube.
The OVIVO “Freedom0” plan gave subscribers 300 minutes of voice calls, 300 text messages and 500 MB of data each month.
Blyk and OVIVO might illustrate one of the strategic issues for ad-supported communications, namely the need for scale. Blyk, for example, could not create enough reach to interest big brands.
In the past, other would-be providers tried supporting fixed network voice services using advertising.
But even some service providers that wanted to create big ad-supported services have had to retrench. In the United States, RingPlus offers zero-cost mobile service offering 300 “no incremental cost” calling minutes or 50 free text messages per month, but using a freemium model, not the ad-supported model it originally favored.
RingPlus users can add credit to their accounts with a credit or debit card. And there is a $49 a month plan for people who want unlimited usage.
But efforts persist. Denver International Airport offers free domestic and global phone calling with a new advertisement-based service offered by RMT Free Phone, available at more than 200 landline phones throughout the airport.
The program is the result of a new partnership between the airport, RMES Communications and DIA's advertising agent Clear Channel Airports.
International calls are free for the first 10 minutes, with a charge of 25 cents for each additional minute, plus a 15 percent tax.
The phone service is supported through ad revenue. Each phone has a 17-inch LCD screen that will run 15-second advertisements and offer digital coupons.
Likewise, icall, supporting low-cost calling on mobile devices, originally pitched as an ad-supported service, now has switched to a Skype-style VoIP service.
Ad-supported content works for broadcasters because they have scale. Ad-supported software works for Google because Google has scale. Until an ad-supported communication service provider can attain similar scale, it seems doubtful it can succeed.ad-
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Yes, Follow the Data. Even if it Does Not Fit Your Agenda
When people argue we need to “follow the science” that should be true in all cases, not only in cases where the data fits one’s political pr...
-
We have all repeatedly seen comparisons of equity value of hyperscale app providers compared to the value of connectivity providers, which s...
-
It really is surprising how often a Pareto distribution--the “80/20 rule--appears in business life, or in life, generally. Basically, the...
-
One recurring issue with forecasts of multi-access edge computing is that it is easier to make predictions about cost than revenue and infra...