Despite growing threats of online competition, some 87 percent of U.S. households nationwide subscribe to some form of multichannel video subscription service, according to Leichtman Research Group.
That is up from 80 percent take rates in 2004. As you might suspect, income plays a part in non-adoption.
The mean annual household income of multichannel video subscribers is 53 percent higher than the household income of non-subscribers.
Nationwide, six percent of homes with annual incomes over $75,000 do not subscribe to a multichannel video service, compared to 12 percent with incomes of $30,000-$75,000, and 27 percent of homes with incomes under $30,000.
Of those figures, the perhaps increasingly-important number is the percentage of homes that can afford the product, who choose, for some reason, not to buy. There is a growing sense that many such households include younger Millennial consumers, who do not appear to have the same propensity to buy the service as older users tend to exhibit.
The findings are based on a telephone survey of 1,369 households from throughout the United States, and are part of a new LRG study.
The other issue is the impact a sluggish economy might be having. Some 42 percent of surveyed individuals agree that changes in the economy have negatively impacted their household in the past year.
About 39 percent of those negatively impacted by the economy agree that they reduced spending on TV, Internet, and phone in the past year.
Also, some 32 percent of those negatively impacted by the economy agree that they will likely reduce spending in the next six months.
About 16 percent of those negatively impacted by the economy report they are likely to switch video providers in the next six months.
On the other hand, men 18 to 34 are now spending more time streaming video than watching live TV, one third visit YouTube multiple times a day, half subscribe to a YouTube channel, and two thirds shared YouTube videos in the past week, according to Generation V , a comprehensive YouTube study of consumer video trends,
The study also finds that 40 percent of women 25 to 49 have subscribed to a YouTube channel, half shared a video this past week, and one third regularly share online video with their kids or parents.
Those changes in viewership illustrate just one aspect of the range of underlying changes that are needed before over the top online video can seriously challenge traditional TV and subscription video services.
Those changes obviously include extensive availability of high-speed broadband access service good enough to support consistently high quality video experiences. Consumers have to create new habits about watching TV and video, including willingness to consume on a variety of devices and screens, with the Internet being the delivery mechanism.
At some point, the ability to view Internet-delivered video on any screen must include easy viewing on the largest screens in a home, and that means further development of in-home devices that make this possible.
Also, users will have to create new habits relating to the sorts of programs they want to watch. The traditional difference between user-generated amateur video and professionally-produced programs will have to narrow.
That could happen in a couple of ways. People could decide they prefer the over the top programming, or traditional programmers could start making their content available for over the top consumption.
Also, artists and performers could themselves start to create programming directly for over the top delivery, narrowing the gap between traditional and newer formats. YouTube, for example, is trying to bridge the gap.
YouTube formats for original programming include themes that resemble traditional video subscription networks. In other words, YouTube will deliberately try to create online versions of traditional cable TV channels, at least to the degree that “channels” and “networks” have a theme.
Revenue sources will develop rather naturally as all those elements come into existence on a significant scale.
In a sense, over the top alternatives represent the latest fragmentation of the TV audience that began decades ago with the advent of the VCR and cable TV. Online video is only the next great wave of audience fragmentation.
Monday, August 20, 2012
Subscription Video Take Rates Still at 87%
 Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Carrier Ethernet Revenue to Double in 3 Years
U.S. enterprises and consumers are expected to spend more than $47 billion over the next five years on Ethernet services provided by carriers, according to a new market research study from The Insight Research Corporation.
With metro-area and wide-area Ethernet services readily available from virtually all major data service providers, industry revenue is expected to grow from nearly $5 billion in 2012 to reach just over $11 billion by 2017.
However, year over year spending growth is expected to gradually stall and by 2017 the annual revenue growth rate will be half of what it is today, Insight Research says.
According to the study, Ethernet's central driver continues to be its ability to meet seemingly endlessly growing bandwidth demands at lower cost and with greater flexibility than competing services.
A major growth driver in years past had been the large-scale migration of wireless backhaul cell sites from TDM to Ethernet, and though still a contributory growth factor, backhaul growth will start to moderate as LTE deployments are completed.
"Wireless backhaul had been a major factor in this fast-growing telecommunications services sector, but with much of the conversion of TDM to Ethernet completed, we are forecasting that spending on Ethernet will moderate," says Robert Rosenberg, president of Insight Research. "Over the five year forecast period we project a compounded annual revenue growth rate of 17 percent, with growth slowing by 2016 to be more in the range of 12 to 15 percent.”
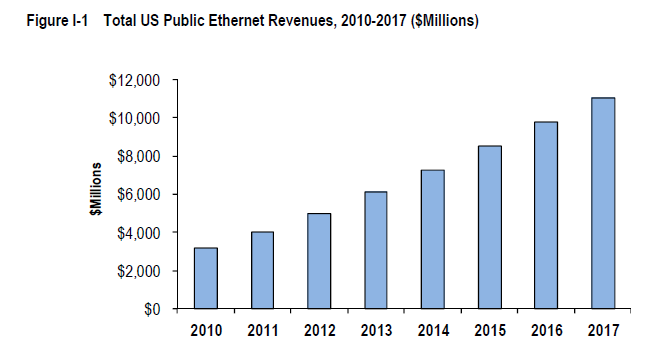
With metro-area and wide-area Ethernet services readily available from virtually all major data service providers, industry revenue is expected to grow from nearly $5 billion in 2012 to reach just over $11 billion by 2017.
However, year over year spending growth is expected to gradually stall and by 2017 the annual revenue growth rate will be half of what it is today, Insight Research says.
According to the study, Ethernet's central driver continues to be its ability to meet seemingly endlessly growing bandwidth demands at lower cost and with greater flexibility than competing services.
A major growth driver in years past had been the large-scale migration of wireless backhaul cell sites from TDM to Ethernet, and though still a contributory growth factor, backhaul growth will start to moderate as LTE deployments are completed.
"Wireless backhaul had been a major factor in this fast-growing telecommunications services sector, but with much of the conversion of TDM to Ethernet completed, we are forecasting that spending on Ethernet will moderate," says Robert Rosenberg, president of Insight Research. "Over the five year forecast period we project a compounded annual revenue growth rate of 17 percent, with growth slowing by 2016 to be more in the range of 12 to 15 percent.”
 Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Mobile Calling Falls for First Time in U.K. Market
Overall time spent using voice communications fell by five percent in 2011, Ofcom, the U.K. communications regulator, reports. “This reflects a 10 percent fall in the volume of calls from landlines, and for the first time ever, a fall in the volume of mobile calls (by just over one percent, in 2011,” Ofcom reports.
Text-based communications are surpassing traditional phone calls or meeting face to face as the most frequent ways of keeping in touch, for U.K. adults, Ofcom, the U.K. communications regulator, says.
The average UK consumer now sends 50 texts a week, more than doubled in four years, with over 150 billion text messages sent in 2011.
Almost another 90 minutes per week is spent using social networking sites and e-mail or using a mobile to access the Internet.
According to Ofcom, 96 percent users 16 to 24 are using some form of text based application on a daily basis to communicate with friends and family; with 90 percent using texts and nearly three quarters (73 percent) using social networking sites.
By comparison, talking on the phone is less popular among this younger age group, with 67 percent making mobile phone calls on a daily basis, and only 63 percent talking face to face.
Text-based communications are surpassing traditional phone calls or meeting face to face as the most frequent ways of keeping in touch, for U.K. adults, Ofcom, the U.K. communications regulator, says.
The average UK consumer now sends 50 texts a week, more than doubled in four years, with over 150 billion text messages sent in 2011.
Almost another 90 minutes per week is spent using social networking sites and e-mail or using a mobile to access the Internet.
According to Ofcom, 96 percent users 16 to 24 are using some form of text based application on a daily basis to communicate with friends and family; with 90 percent using texts and nearly three quarters (73 percent) using social networking sites.
By comparison, talking on the phone is less popular among this younger age group, with 67 percent making mobile phone calls on a daily basis, and only 63 percent talking face to face.
 Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
SIP Trunking Saves 33%
Among enterprises, use of SIP trunking has provided an average 33 percent cost savings over legacy access methods, a study conducted by Webtorials, and sponsored by Sonus Networks, has found.
For 73 percent of respondents, “saving money” was among the key drivers for adoption. But roughly half indicated that ability to use “SIP-specific” features also was an adoption driver.
SIP Trunking, by contrast, is still in the early stages of deployment. In fact, roughly two-thirds of the respondents reported either "Significant Use" or "Extensive Use" of VoIP, while only about one-third of the respondents reported either "Significant Use" or "Extensive Use" of SIP Trunks. Among those using SIP Trunks, significant cost savings have been realized, with an average savings on the order of 33%, Sonus Networks reports.
Some 68 percent of respondents indicated their decisions are driven "mostly by cost savings" or "about equally" by cost and capabilities.
VoIP (89 percent), Unified Communications (69 percent) and video conferencing (65 percent) are the most important types of media to be controlled using SIP.
For 73 percent of respondents, “saving money” was among the key drivers for adoption. But roughly half indicated that ability to use “SIP-specific” features also was an adoption driver.
SIP Trunking, by contrast, is still in the early stages of deployment. In fact, roughly two-thirds of the respondents reported either "Significant Use" or "Extensive Use" of VoIP, while only about one-third of the respondents reported either "Significant Use" or "Extensive Use" of SIP Trunks. Among those using SIP Trunks, significant cost savings have been realized, with an average savings on the order of 33%, Sonus Networks reports.
Some 68 percent of respondents indicated their decisions are driven "mostly by cost savings" or "about equally" by cost and capabilities.
VoIP (89 percent), Unified Communications (69 percent) and video conferencing (65 percent) are the most important types of media to be controlled using SIP.
 Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Leading French Mobile Ops are Between a Rock and a Hard Place
French mobile service providers are between a rock and a hard place. Facing significant competitive pressure that is hitting gross revenues, the incumbent mobile service providers also need to reduce costs to maintain profit margins. But they do not have complete freedom where it comes to those cost cuts.
The French Ministry for the Digital Economy has warned French telecom service providers they may make no job cuts as they restructure to meet the competition.
Iliad, which launched its “Free Mobile” service in January 2012 in France, has been wrecking havoc on its competitors France Telecom, SFR and Bouygues Telecom.
Precisely how the French service providers can make cuts, without touching personnel costs, is a key question, since presumably regulators also do not want any slackening of network capital investment.
Small wonder that many mobile service providers are looking to unload other international assets, in part to reduce debt burdens. But one also wonders whether reducing debt loads is part of an effort to slice operating costs as well.
The French Ministry for the Digital Economy has warned French telecom service providers they may make no job cuts as they restructure to meet the competition.
Iliad, which launched its “Free Mobile” service in January 2012 in France, has been wrecking havoc on its competitors France Telecom, SFR and Bouygues Telecom.
Precisely how the French service providers can make cuts, without touching personnel costs, is a key question, since presumably regulators also do not want any slackening of network capital investment.
Small wonder that many mobile service providers are looking to unload other international assets, in part to reduce debt burdens. But one also wonders whether reducing debt loads is part of an effort to slice operating costs as well.
 Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Is Broadband Access One Market, or Many?
It isn't always easy to figure out what a "product" is, for purposes of plotting that "product's" life cycle. Is landline voice "one product," or a series of products that have been offered over the years? Similarly, is "Internet access" one product, or several?
The answer matters, as we can assume any product, including broadband access, will have a product life cycle. But we have to agree on what “the product” is, before we can figure out how to understand the life cycle.
Some might argue that “Internet access” is the product, with successive new generations of products simply reflecting better ways of supplying “Internet access.”
That view would make dial-up, slower speed DSL or cable modem services and now 300 Mbps services products one category. Product managers might not agree, and for good reason. One can plot the rise and fall of "dial-up" Internet access quite distinctly from the adoption of high-speed access services.
The precedent, one might argue, is “voice service.” Over time, the industry has evolved through various types of switching and access technology, but the product category always has been “fixed network voice.”
In a business sense, we can count the number of subscribers served by specific switch technologies, but the business-relevant distinction has remained “total number of lines in service” (access lines in service).
Using that analogy, all forms of Internet access represent one product category. But few are likely to accept that definition so readily.
For starters, there is the simple matter of lead applications for various types of Internet access.
The "killer app" for “dial-up Internet access” was email. That isn't exactly true for the early generations of broadband services, which tended to shift the lead apps to visual Web apps.
Now, streaming video and audio seem to be the lead applications, even though a variety of apps are used by most broadband customers. But as we push to speeds routinely above 20 Mbps, it is likely new lead apps will develop.
Also, there is the matter of mobile broadband access, which arguably gets used in different ways than fixed access. Are those examples of two distinct markets, or one market with segments?
The answer might matter since, In many developed markets, the “fixed network Internet access” product is reaching saturation, where every consumer who wants the product already is buying it. To refresh product lines, and earn more revenue, service providers are relying on faster speed services that sell for higher prices.
But the faster-growing segment is mobile broadband. China, for example, has seen fewer fixed broadband subscribers over the past year, instead of growing.
In other words, fixed broadband accounts actually declined, as users apparently decided to spend their money on mobile broadband, rather than fixed broadband.
Chinese Internet users reached 530 million over the past six months, but the broadband subscriber base actually shrank as mobile became the most popular way for users to get online for the first time, a report by the Chinese government suggests.
Of those users, some 380 million were fixed broadband users, down from 396 million in December 2011, and 388 million were mobile internet users, up from 356 million.
So “mobile broadband access” appears to be a substitute and new product, with a different life cycle, than fixed broadband.
The answer matters, as we can assume any product, including broadband access, will have a product life cycle. But we have to agree on what “the product” is, before we can figure out how to understand the life cycle.
Some might argue that “Internet access” is the product, with successive new generations of products simply reflecting better ways of supplying “Internet access.”
That view would make dial-up, slower speed DSL or cable modem services and now 300 Mbps services products one category. Product managers might not agree, and for good reason. One can plot the rise and fall of "dial-up" Internet access quite distinctly from the adoption of high-speed access services.
The precedent, one might argue, is “voice service.” Over time, the industry has evolved through various types of switching and access technology, but the product category always has been “fixed network voice.”
In a business sense, we can count the number of subscribers served by specific switch technologies, but the business-relevant distinction has remained “total number of lines in service” (access lines in service).
Using that analogy, all forms of Internet access represent one product category. But few are likely to accept that definition so readily.
For starters, there is the simple matter of lead applications for various types of Internet access.
The "killer app" for “dial-up Internet access” was email. That isn't exactly true for the early generations of broadband services, which tended to shift the lead apps to visual Web apps.
Now, streaming video and audio seem to be the lead applications, even though a variety of apps are used by most broadband customers. But as we push to speeds routinely above 20 Mbps, it is likely new lead apps will develop.
Also, there is the matter of mobile broadband access, which arguably gets used in different ways than fixed access. Are those examples of two distinct markets, or one market with segments?
The answer might matter since, In many developed markets, the “fixed network Internet access” product is reaching saturation, where every consumer who wants the product already is buying it. To refresh product lines, and earn more revenue, service providers are relying on faster speed services that sell for higher prices.
But the faster-growing segment is mobile broadband. China, for example, has seen fewer fixed broadband subscribers over the past year, instead of growing.
In other words, fixed broadband accounts actually declined, as users apparently decided to spend their money on mobile broadband, rather than fixed broadband.
Chinese Internet users reached 530 million over the past six months, but the broadband subscriber base actually shrank as mobile became the most popular way for users to get online for the first time, a report by the Chinese government suggests.
Of those users, some 380 million were fixed broadband users, down from 396 million in December 2011, and 388 million were mobile internet users, up from 356 million.
So “mobile broadband access” appears to be a substitute and new product, with a different life cycle, than fixed broadband.
 Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Hosted IP PBX Services Will Grow 300% to 2016
U.S. spending on unified communications technologies will increase by an average of 10 percent per year, led by spending on hosted IP telephony services, which will almost triple between 2011 and 2016, estimates InfoTrack.
Separately, Infonetics Research predicts the number of seats for hosted business VoIP and unified communications services is on track to more than double between 2012 and 2016. Note that forecast includes both hosted IP telephony and UC.
Among U.S. enterprises, defined as firms with 500 or more employees, spending on hosted IPT will grow at an average rate of 27 percent, which is almost two times faster than the average increase among U.S. SMBs (firms with fewer than 500 employees), InfoTrack says.
But over the next five years, the growth of SMB spending on UC apps will be more than twice the rate of U.S. enterprises, which represents the mirror image of what we project happening in the hosted IPT sector," said Ken Dolsky, Senior Program Director for InfoTrack.
As always, one has to keep the size of the installed base in mind when pondering such forecasts. Other researchers, including Parallels, have estimated that small and medium business hosted IP telephony penetration is still relatively small.
The global market for hosted PBX (hosted IP telephony) services averaged between four percent and seven percent in the largest SMB markets, Parallels noted, as recently as late 2011.
Infonetics Research separately has forecast that the global SMB VoIP services market would grow to $76.1 billion in 2015 with total subscribers of 262 million. Keep in mind that the total global telecom services business accounts for about $2 trillion in annual revenue in 2012.
So hosted IP telephony would represent about four percent of global revenues.
In the United States, it has been estimated that around 500,000 SMBs currently use a hosted PBX service, representing an $800 million market. In a U.S. telecom service business of about $336 billion in annual revenue, hosted IP telephony represents about two-tenths of one percent of total industry revenue.
However, Parallels estimates that the majority of the current in-house PBX systems will migrate to hosted mechanisms over time, representing $3.9 billion potential market for hosted PBX.

US Hosted PBX Market – Source: Parallels SMB Cloud Insights Report, 2011
Separately, Infonetics Research predicts the number of seats for hosted business VoIP and unified communications services is on track to more than double between 2012 and 2016. Note that forecast includes both hosted IP telephony and UC.
Among U.S. enterprises, defined as firms with 500 or more employees, spending on hosted IPT will grow at an average rate of 27 percent, which is almost two times faster than the average increase among U.S. SMBs (firms with fewer than 500 employees), InfoTrack says.
These days, though, estimating the size of the global market for business IP telephony services offered by service providers is a hard question to answer. For starters, IP telephony can include sales of IP private branch exchanges, unified communications solutions and services, hosted IP telephony services, access services such as SIP trunking and fees earned for managing premises business phone systems.
With all of this, the global business IP telephony market will reach $20.8 billion by the year 2018, according to Global Industry Analysts. The problem, of course, is that it is tough to make sense of global estimates, especially without knowing in some detail which specific products are included in that figure.
The global market for hosted PBX (hosted IP telephony) services averaged between four percent and seven percent in the largest SMB markets, Parallels noted, as recently as late 2011.
The global market for hosted PBX (hosted IP telephony) services averaged between four percent and seven percent in the largest SMB markets, Parallels noted, as recently as late 2011.
Infonetics Research separately has forecast that the global SMB VoIP services market would grow to $76.1 billion in 2015 with total subscribers of 262 million. Keep in mind that the total global telecom services business accounts for about $2 trillion in annual revenue in 2012.
So hosted IP telephony would represent about four percent of global revenue.
In the United States, it has been estimated that around 500,000 SMBs currently use a hosted PBX service, representing an $800 million market. In a U.S. telecom service business of about $336 billion in annual revenue, hosted IP telephony represents about two-tenths of one percent of total industry revenue.
In the United States, it has been estimated that around 500,000 SMBs currently use a hosted PBX service, representing an $800 million market. In a U.S. telecom service business of about $336 billion in annual revenue, hosted IP telephony represents about two-tenths of one percent of total industry revenue.
However, Parallels estimates that the majority of the current in-house PBX systems will migrate to hosted mechanisms over time, representing $3.9 billion potential market for hosted PBX.
At the moment, it remains the case that most business IP telephony is supplied by premises-based solutions.
So how big is the business IP telephony? It depends on who you ask, and what the assumptions are.
"In 2011, SMBs represented 46 percent of the U.S. installed base of IPT lines, but accounted for only 30 percent of the spending on UC applications,” InfoTrack says. But over the next five years, the growth of SMB spending on UC apps will be more than twice the rate of U.S. enterprises, which represents the mirror image of what we project happening in the hosted IPT sector," said Ken Dolsky, Senior Program Director for InfoTrack.
As always, one has to keep the size of the installed base in mind when pondering such forecasts. Other researchers, including Parallels, have estimated that small and medium business hosted IP telephony penetration is still relatively small.
The global market for hosted PBX (hosted IP telephony) services averaged between four percent and seven percent in the largest SMB markets, Parallels noted, as recently as late 2011.
Infonetics Research separately has forecast that the global SMB VoIP services market would grow to $76.1 billion in 2015 with total subscribers of 262 million. Keep in mind that the total global telecom services business accounts for about $2 trillion in annual revenue in 2012.
So hosted IP telephony would represent about four percent of global revenues.
In the United States, it has been estimated that around 500,000 SMBs currently use a hosted PBX service, representing an $800 million market. In a U.S. telecom service business of about $336 billion in annual revenue, hosted IP telephony represents about two-tenths of one percent of total industry revenue.
However, Parallels estimates that the majority of the current in-house PBX systems will migrate to hosted mechanisms over time, representing $3.9 billion potential market for hosted PBX.
US Hosted PBX Market – Source: Parallels SMB Cloud Insights Report, 2011
 Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Gary Kim has been a digital infra analyst and journalist for more than 30 years, covering the business impact of technology, pre- and post-internet. He sees a similar evolution coming with AI. General-purpose technologies do not come along very often, but when they do, they change life, economies and industries.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
How Many Consumers "Use" Generative AI?
Daily use of generative artificial intelligence platforms might still be in the 11 percent of U.S. internet users, says Morgan Stanley Resea...
-
We have all repeatedly seen comparisons of equity value of hyperscale app providers compared to the value of connectivity providers, which s...
-
It really is surprising how often a Pareto distribution--the “80/20 rule--appears in business life, or in life, generally. Basically, the...
-
One recurring issue with forecasts of multi-access edge computing is that it is easier to make predictions about cost than revenue and infra...