There is a difference between execution risk and strategic risk. In the former instance a firm or person might have had the right idea, but chose the wrong set of actions. In the latter instance a firm or person chooses an incorrect plan.
In that regard, telecom firms sometimes make mistakes of execution or strategy. Mistakes in the former can obscure the validity of the latter. Consider Verizon’s sale of 90 percent of its AOL assets.
Some will argue diversifying into content is not a good strategy for connectivity providers. But in 2017 50 telcos around the globe generated more than $90 billion in content revenues, mostly from video services.
Organic growth in core connectivity services cannot contribute much, in a growing number of connectivity markets, to revenue. The phrase terminal decline has been applied to legacy connectivity services, for example. And that leads to a search for new revenue sources.
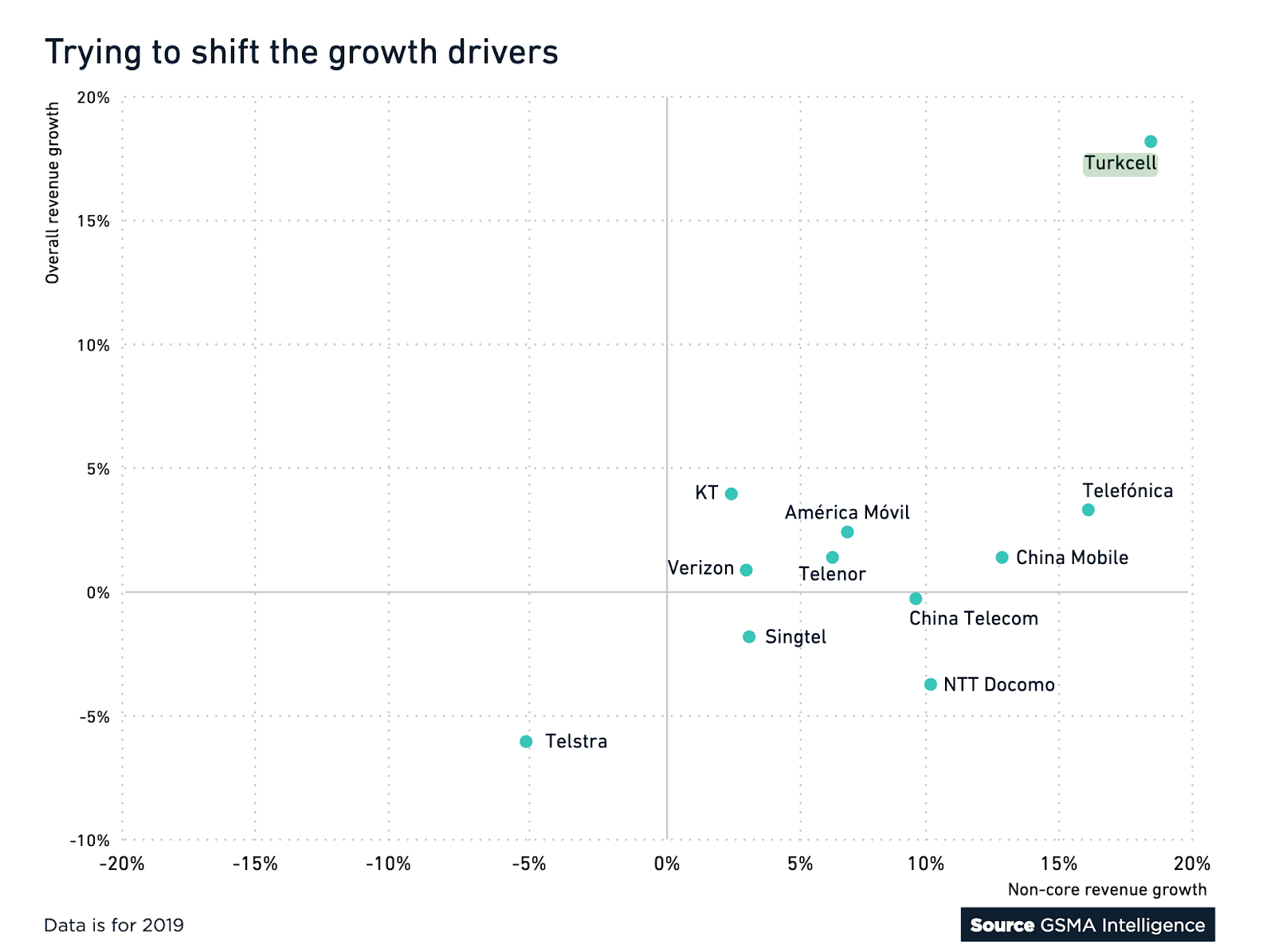
source: GSMA Intelligence
Also, unless one wishes to use an obsolete “what is a telco?” definition, cable TV companies have transformed themselves from video distributors into content owners, mobile service providers, business connectivity providers and leading suppliers of broadband access as well.
The notion that connectivity providers “cannot” master the content business is incorrect. It can be argued that telcos have had more financial success in content than in their roles as app store providers, equipment manufacturers, computing suppliers or data center suppliers.
Though legacy telcos do participate to some extent in the enterprise phone system business, system integration, virtual private network and other connectivity lines of business, they often do so as lesser providers in segments dominated by others (either communication specialists or information technology providers).
The point is that telcos arguably have been more successful in video entertainment than in all other diversification efforts of the past four decades.

source: GSMA
In 2018 nearly half of telco executives surveyed by EY cited television and video services as among the top three best ways to grow new revenues. The alternative is failure, if present revenue and profit trends continue.
Global telco revenue growth rates remain stubbornly close to one percent per year, below the long-term rate of inflation. If one were looking any key component of telecom revenues, one would see a historical curve reminiscent of a standard product life cycle, with declining demand, declining profits or both.
Product maturation, product substitutes and changes in value are issues telcos have dealt with for a couple of decades already. So if the core business is under strategic attack, what strategy is called for?
The range of options have not really changed much in four decades. Telcos can run today’s business more efficiently; grow the current business through acquisition or innovation or get into new lines of business.
All three have worked for various providers; at various times. The biggest single revenue driver was entry into the mobile business. First voice subscriptions for business users; then consumer users; then text messaging and now internet access have provided waves of revenue growth in the mobile segment.
More recently, internet access has been important for fixed network service providers, but most fixed network providers have grown through acquisition. In fact, they arguably have grown mostly by acquisition.
To put the Verizon move into content, the argument can be made that the AOL plus Yahoo failure to make a bigger revenue contribution was that Verizon purchased the wrong assets, at too low a scale. Both AOL and Yahoo were “legacy” internet assets, “closed” or “walled garden” in a market moving to “open.”
Both assets were past the peak of their product life cycles. AOL’s subscriber base peaked in 2002, nearly 20 years ago. Yahoo revenue peaked in 2008, more than a decade ago. Both assets were generating less than $10 billion in annual revenue for Verizon, were declining and in no position to lead growth in the content business, having perhaps three percent share of the digital advertising business, for example.
The point is that Verizon’s experience with Yahoo and AOL is not necessarily evidence of strategic failure. It almost certainly is an execution mistake. The acquisitions were not of high growth properties with a chance to lead their markets. Nor was there sufficient scale to compete effectively with the other leading digital ad platforms.
There might be company culture issues at work, as well. Compared to AT&T, which grew by acquisition, Verizon has preferred organic growth. Where Verizon has emphasized the quality of its network and a smaller footprint, AT&T has looked for scale, with market-competitive network performance.
AT&T--like Comcast--committed to content ownership at scale. Verizon--like Charter Communications--preferred a connectivity strategy.
Still, it is possible to note that, over time, fewer connectivity providers will be able to maintain revenue growth relying solely on connectivity revenues. The only issue is where to look for new lines of business.
