Firms backed by private equity have different business models than other long-term operators of connectivity assets. PE-backed firms aim to create value (typically double the asset value within seven years) and then sell the assets.
That is a different model than used by connectivity service providers who operate for the long term, where fundamental issues of free cash flow, revenue growth and profit, as well as the ability to pay dividends, are the key constraints.
And so it is with investors in fiber-to-home assets.
Back in the heady days of 1996, when the Telecommunications Act of 1996 became law, business models for firms providing connectivity services changed in a big way. For legacy providers, maintaining market share became the key issue. For attackers, gaining share became the obvious key issue.
Beyond that, the imperatives were different. Legacy providers, operating their businesses for the long haul, could not adopt the “fast growth rather than profits” models as used by many attackers. At a time of “easy money” and “we want you to grow fast” attitudes of key investors, that made sense for attackers.
And, as has been true for many software startups, long-terms operating profits were not the goal. Instead, fast growth in a “hot” area was the objective, since such firms had reasonable expectations they would simply be bought out at some point before they ever reached “terminal value.”
That, at least, is what one has to assume when looking at the costs of FTTH networks and costs to actually connect customers and earn a profit on those services.
The reported cost per-home-passed (CPHP) for underground FTTH deployments ranged from $1,600 to $2,600, according to a recent estimate by Cartesian researchers. The CPHP for aerial deployments was lower than those of underground, ranging from under $700 to $1,500 for respondents in suburban and urban environments, and $1,300 to $2,700 in more rural areas.
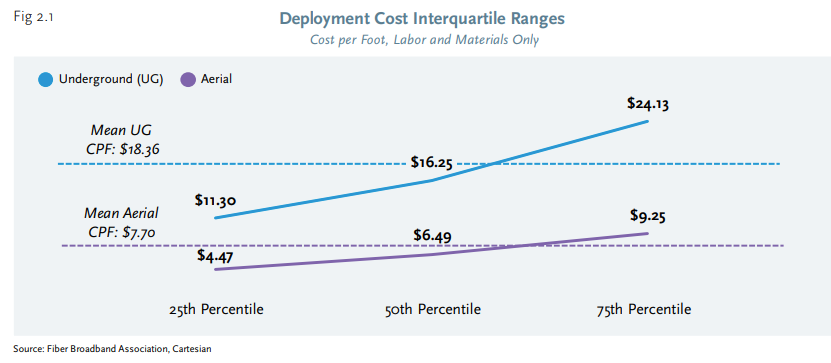
source: Fiber Broadband Association
Actually connecting a paying customer adds another $600 to $830 in drop costs.
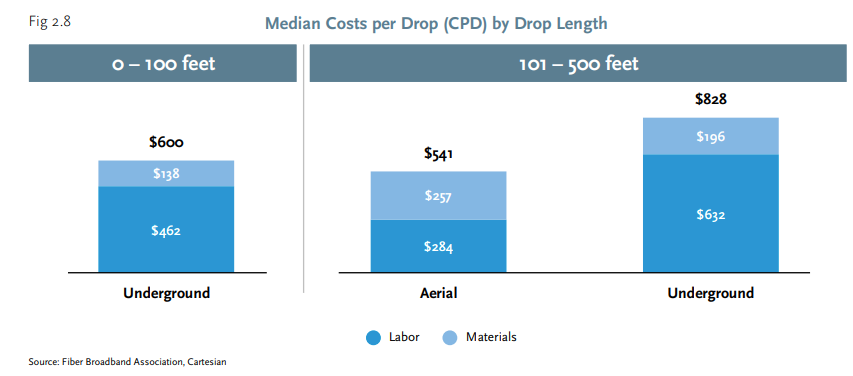
source: Fiber Broadband Association
So the per-home cost of serving a paying customer includes an attributed cost of building the network; an assumption about take rates and then the cost of the drop and installation; plus operating and marketing costs.
Take rates matter. At a 50-percent take rate, for example, the per-customer cost of the network can range from $2,600 to perhaps $5,200, with an additional $600 to $800 in drop costs, for a per-customer network cost ranging from a “best case” of perhaps $3,200 up to perhaps $6,000.
But that is just the network platform. One would have to add in operating and marketing costs, plus any debt service and loan principal repayments. Operating and marketing costs might range from about $210 per year to $800 per year, per customer, according to some estimates.
Cost Category | Low Estimate ($/year/subscriber) | High Estimate (/year/subscriber) | Sources |
Network Infrastructure | $100 | $500 | FTTH Council: $200-$300, Deloitte: $300-$500 |
Operations & Maintenance (O&M) | $25 | $75 | FTTH Council: $40-$60. Analysys Mason: $25-$35 |
Customer Acquisition (CAC) | $50 | $150 | BroadbandNow: $50-$100, Analysys Mason: $60-$150 |
Customer Care & Billing | $25 | $50 | Analysys Mason: $25-$35, Leichtman Research Group: $30-$40 |
Marketing & Sales | $10 | $30 | Analysys Mason: $10-$20, Leichtman Research Group: $15-$25 |
Total Operating Cost | $210 | $805 | Sum of individual ranges |
And one might have to add interest charges and eventual debt principal repayment in addition to those charges.
And there is a possible additional range of investments as well. Some firms must first acquire copper-based legacy telco assets first, before starting the FTTH upgrade, either to own and operate over the long term, or to sell the assets in five to seven years.
Transaction | Date | Buyer | Seller | Asset Type | Homes Passed (M) | Price (USD Billion) | Cost per Passing (USD) | Source |
Brightspeed - Lumen assets (20 states) | Oct 2022 | Brightspeed | Lumen | Fiber | 0.3 | 3.0 | 10,000 | Reuters |
Consolidated Communications - NewWave Communications | Aug 2022 | Consolidated | NewWave | Fiber | 0.18 | 0.65 | 3,611 | Fierce Telecom |
Windstream - MetroNet Holdings (FL) | Aug 2022 | Windstream | MetroNet | Fiber | 0.06 | 0.28 | 4,667 | Fierce Telecom |
Frontier Communications - Verizon (WA, OR) | Dec 2021 | Frontier | Verizon | Mixed (Fiber & Copper) | 0.14 | 1.05 | 7,500 | Fierce Telecom |
Allo Communications - Lincoln Telephone & Telegraph | Nov 2021 | Allo | Lincoln | Mixed (Fiber & Copper) | 0.11 | 0.21 | 1,909 | TelecomTV |
Ziply Fiber - US Cellular assets (WA, OR) | Oct 2021 | Ziply | US Cellular | Fiber | 0.12 | 0.51 | 4,250 | Fierce Telecom |
CNSL - Searchlight Investment | Jan 2020 | Searchlight | CNSL | Mixed (Fiber & Copper) | 0.71 | 0.425 | 600 | CNBC |
In many cases, the capital investment to acquire assets is equal to, or more than, the cost to add the FTTH upgrade. But that’s where the business case lies. If one assumes a copper asset can be purchased for $600 to $800 per passing, but then an upgraded FTTH asset can be sold for $5,000 to $10,000 per passing, that is the business case for making all the investments in FTTH.
It might still be a difficult business case for a shorter-term owner, but “buying copper assets; upgrading to FTTH and then selling” can work.
The payback for longer-term operators always has been equally challenging, if not more challenging, and has gotten arguably tougher as total account revenues including voice and video entertainment have dwindled, forcing the payback model to be based on home broadband alone.
The main point is that FTTH payback models for private equity investors and service providers are quite distinct. What makes sense for a PE firm might not always make sense for a legacy fixed network service provider or an “overbuilder.”
That is perhaps one reason why GFiber (owned by Alphabet) has not purchased copper telco fixed network assets before upgrading them. As with other “overbuilders,” GFiber has simply built its own greenfield FTTH networks from scratch.
