Right now, one might argue that the greatest impact of artificial intelligence will come in the realm of efficiency: allowing humans to do all sorts of things faster. To some extent, that has been at least a secondary feature of most computing technologies since 1980.
But it might be argued that the primary outocmes of new computing technologies have centered on digital product substitution for analog or physical products, removing constraints of time and place.
Products such as music, newspapers, magazines, books, television and movies were changed from physical to virtual products, or from physical delivery to virtual delivery.
Since virtual goods are often cheaper to create, distribute and replicate than physical goods, new business models are possible. Video and music streaming; online publishing; user-generated content; social media and search are examples.
Traditional Industry | New Challengers | Competitive Advantage |
Retail (Brick-and-Mortar Stores) | Online Retailers (Technology) | E-commerce platforms, data analytics for targeted marketing, efficient logistics networks. |
Media (Newspapers) | Social Media Platforms (Technology) | Real-time news updates, user engagement through interactive features, targeted advertising. |
Taxis (Regulated Industry) | Ride-Sharing Apps (Technology) | Mobile app for booking rides, efficient matching of drivers with passengers, dynamic pricing models. |
Financial Services (Traditional Banks) | Fintech Startups (Technology) | Mobile banking apps, online payment processing, data-driven credit scoring models. |
Hospitality (Hotels) | Home-Sharing Platforms (Technology) | Online booking platform, user reviews and ratings, lower lodging costs for travelers. |
Aside from new “products,” we also saw at least a few new business models, such as ad-supported technology, which did not exist prior to the internet. You might not think of social networks; messaging or search as “technology” products, but they are. Likewise, we saw the development of commerce-supported technology models as well.
Though AWS and Google Cloud might use a traditional fee-for-service revenue model, that is possible only because the prior creation of ad-supported search and commerce produced excess capacity that underpinned cloud computing “as a service.”
Likewise, earlier waves of innovation removed time and place constraints. E-commerce allows shopping anytime, anywhere while communication tools such as messaging, email and video conferencing enable collaboration across great geographical distances almost for free.
So how might AI alter business models, consumer experience and industries? Right now, it seems as though extreme personalization; customization and automated functions will be the primary effects.
AI will further personalize software experiences, creating hyper-personalized experiences for consumers, and therefore supplier opportunities across many industries.
Automation and efficiency should be the other key AI contribution, allowing firms to optimize and reduce costs across their operations. Aside from the consumer price benefits, that will enable new possibilities for cross-industry disruption.
Cloud computing “as a service” allowed Amazon (retailer) and Google (search provider) to emerge as suppliers of computing services in competition with traditional suppliers of computing hardware and software, for example.
Microsoft, until recently a primarily a supplier of enterprise and consumer software, emerged as a supplier of computing services and content. Apple the PC company became a leading mobile phone supplier.
Cable TV firms became full-fledged suppliers of fixed and mobile communications services. Many non-banks essentially became “banks.”
Traditional Industry | Firm | Services Offered |
Retail (Large Chains) | Walmart MoneyCard, Amazon Cash | Prepaid debit cards for purchases and bill pay. |
Technology (Payment Apps) | PayPal, Venmo, Square | Money transfer, bill pay, debit card linked accounts. |
Retail (Fintech Startups) | Chime, Current, SoFi | Mobile banking accounts, debit cards, potential credit products. |
Retail (Fintech Startups) | Klarna, Afterpay | Point-of-sale financing and "buy now, pay later" options. |
Finance (Investment Firms) | Charles Schwab, TD Ameritrade | Robo-advising, checking accounts, debit cards. |
Retail (Ride-Sharing) | Uber Debit Card | Debit card with rewards and features for drivers. |
It is hard to tell, at this moment, whether AI will enable entirely new categories of products and services in the same way that the internet produced “search” and “social media,” with their different revenue models.
All we know now is that AI will be applied to virtually every existing industry, business process and consumer product in some way. So AI will be a feature of most products; an application in other cases. AI will have vertical industry forms, where AI-optimized processes are industry-specific, as well as horizontal applications supporting marketing, operations or finance for any industry.
AI might in some cases be used as an interface, in the same way that graphical user interfaces changed the human interaction with personal computers. In other cases AI might be an alternative replacement for “search.”
There are lots of other analogies. Generative AI, for example, might function as a word processor; a photo editing app; a musical instrument; a mini version of an operating system, human subject matter expert or code writer.
Generative AI Function | User Analogy | Description |
Text Generation | Word Processor | Instead of typing from scratch, AI generates different creative text formats like poems, scripts, musical pieces, or code based on prompts and user input. |
Image Generation | Photo Editing App | AI acts like a powerful photo editor that can create new images from scratch based on descriptions or edit existing ones by adding elements or changing styles. |
Music Generation | Musical instrument | AI generates new music pieces in various genres or moods based on user preferences. |
3D Modeling | CAD Software | Like Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, AI can generate 3D models of objects for various purposes, from prototyping to video game design. |
Data Augmentation | Operating System | Imagine an OS feature that automatically creates synthetic data (like images or text) to supplement existing datasets, improving the training of other AI models. |
Personalization | App Feature | Think of an app feature that personalizes your experience. Generative AI can personalize content feeds, product recommendations, or even tailor learning materials based on individual user preferences. |
Code Completion | Programming Language Feature | Similar to a programming language's code completion feature, AI can suggest or even generate entire sections of code based on the context of the program being written. |
Creative Ideation | Brainstorming Session Assistant | Imagine having an AI assistant during a brainstorming session. It can generate new ideas, variations on existing concepts, or unexpected connections to spark creative thinking. |
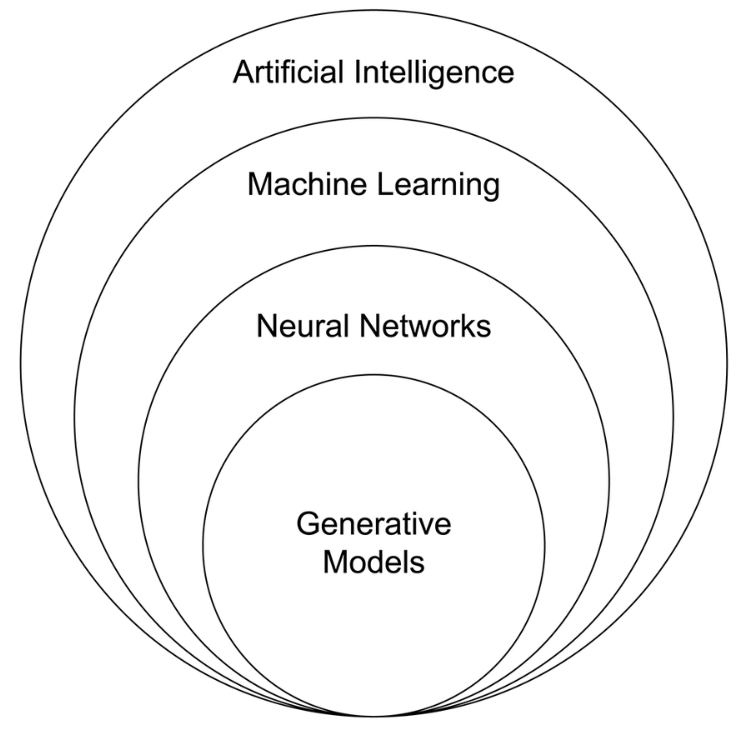
AI might be described as a machine-based system that can make predictions, recommendations, or decisions.
Machine learning then might be defined as data-driven approaches that allow computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
Neural networks are computer systems inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, able to learn from data and improve their ability to perform tasks such as image and speech recognition, as well as natural language processing.
So neural networks underlie generative models designed to create entirely new content, including text, images, videos, music or software code.
source: Wikipedia
