The Covid pandemic was a vivid reminder to all of us who create models, build scenarios or make predictions that we are unable to accurately account for all possible influences and outcomes. By definition, we are unable to account for highly-improbable, very rare events that have high effect on whatever it is that we are modeling.
The pandemic also was a reminder of how difficult it is to create organizations that respond better to unexpected stresses. One tactic for reducing fragility is to possess more cash. That is akin to reducing reliance on "just in time" supply chains, which, as the pandemic showed, increases risk and fragility.
Many businesses and non-profits assume there will be times when revenues slow or increase. Cash reserves or contingency funds are one way to create "antifragile" capabilities. But I know of no organization that prepared for a sudden and complete shutdown of all operations--and a virtual ban on customers buying--extending for months to nearly a year.
Though for many of us the Covid pandemic is the biggest black swan event we have ever seen. A black swan event is unpredictable and unprecedented in scale and retroactively explainable, according to Nassim Taleb.
Nassim actually states the case more dramatically: "nothing in the past can convincingly point to its possibility.” By that standard, some argue Covid is not a black swan; perhaps neither is the Great Recession of 2008; nor the emergence of the internet. We have seen major pandemics in human history. We have experienced severe global recessions and seen the impact of computer technology on human life.
Perhaps the definition does not matter much. After all, Talib’s whole point is resilience; the ability to create organizational ability to adapt to low-probability and high-consequence events. Whether one believes Covid, for example, is a black swan or not, what might we have done to prepare for it. More to the point, what should we be doing to prepare for some unknown future black swan?
Retroactively, we can put into place mechanisms to deal with pandemics. But we cannot spend unlimited amounts of resources doing so. Nor, as a practical matter, can we easily design better systems to account for threats we cannot presently imagine. Yet that is what Taleb counsels. He calls such resilience “antifragile.”
Exercise is one antifragile practice, he argues. Perhaps cash in the bank also is an antifragility measure. Some might say this is “resilience.” Taleb rejects that notion. Antifragility as Taleb views it is a property of systems that get stronger in the face of stressors, shocks, volatility, noise, mistakes, faults, attacks, or failures.
“Antifragility is beyond resilience or robustness,” he argues. “The resilient resists shocks and stays the same; the antifragile gets better.” Antifragility is the ability to demonstrate a non-linear response to events.
“You have to avoid debt because debt makes the system more fragile,” he says. “You have to increase redundancies in some spaces. You have to avoid optimization.” In a real sense, Taleb says antifragility is enhanced by being deliberately less specialized and less structured.
The concept was developed by Nassim Nicholas Taleb in his book, Antifragile, and in technical papers.[1][2] As Taleb explains in his book, antifragility is fundamentally different from the concepts of resiliency (i.e. the ability to recover from failure) and robustness (that is, the ability to resist failure).
Others might say it is disaster preparedness.
One might well argue that there is a normal human resistance to spending too much time, effort or money on preparing for unpredictable; low-probability events with massive impact. By definition, we cannot foresee the sort of event we are preparing for.
No forecaster, therefore, can predict or model the impact of a black swan event: it is, by definition, unpredictable.
We simply assume that present trends will continue, within some zone of variation.
A positive black swan might be the internet; a prior negative black swan was the global Great Recession of 2008. We can all agree that one essential element of a black swan event is that it has a sudden and unexpected magnitude outside our models.
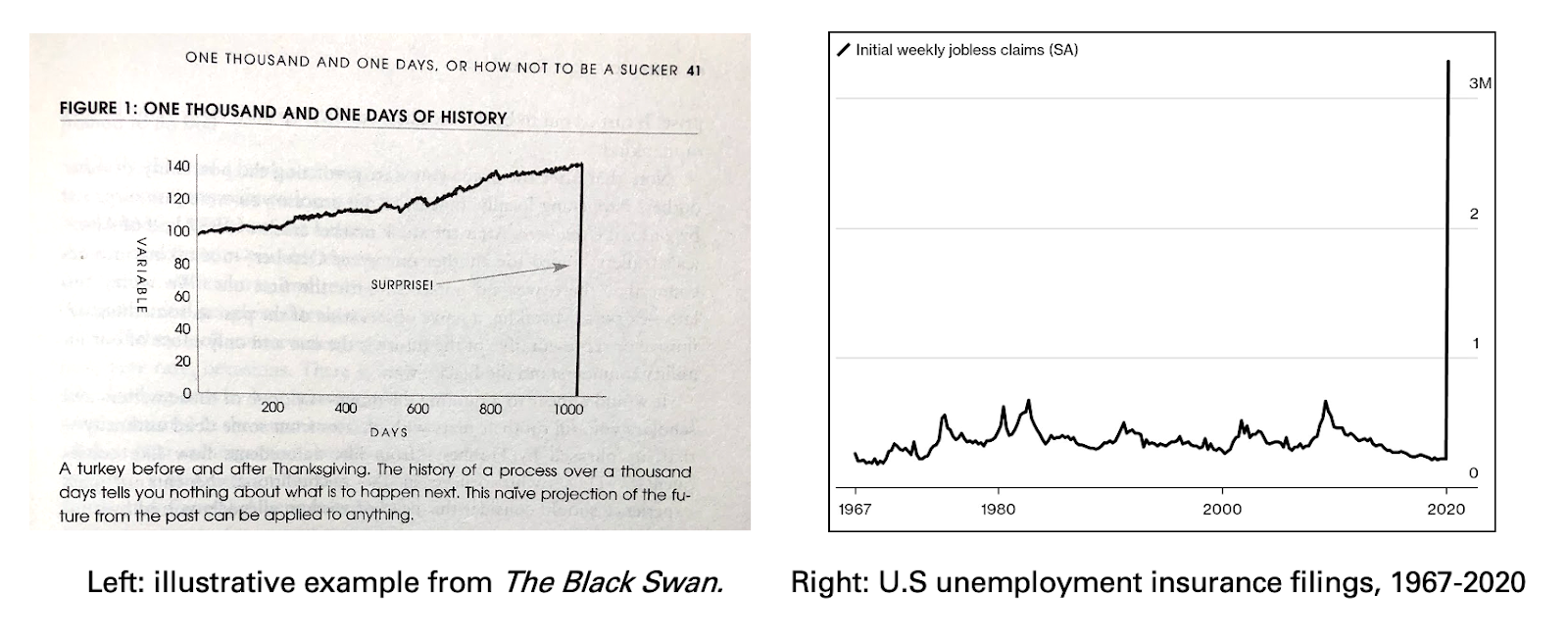
source: Alex Danco
The main idea is that black swan events are extremely unpredictable and have massive impacts on society.
A corollary might be that black swan events are “preemptively ruled out” in human mental models or forecaster predictions.
“For an event to really be a Black Swan event, it has to play out in a domain that we thought we understood fluently, and thought we knew the edge cases and boundary conditions for possible realm,” argues Alex Danco.
Immediate "economic curtailment worse than the Great Recession of 2008" was outside the thinking of anybody I have encountered.
