Promoters of every digital next-generation mobile network have promised and hoped for the creation of new use cases and applications. And that arguably has happened, though often not as fast as expected or in the way expected.
Still, new use cases always have developed with each successive next generation mobile platform. Early in the 5G era, most observers now recognize that 5G fixed wireless has become the first obvious new use case for 5G.
Most observers believe the internet of things, private networks, edge computing and virtual private networks are likely additional use cases. Opinion is more divided about the use of 5G to support more-immersive applications (gaming, digital twins) and understandably quite divided about whether the full metaverse of persistent, three-dimensional experiences will require 5G, and if so, to what extent and by what date.
The only clear pattern is higher data consumption.
Higher data consumption also seems a hallmark of each next generation platform. With the caveat that some of the increase is driven by greater numbers of subscribers, the trend of higher usage has been in place since at least 2005. Still, nobody would contest the argument that users consume more data on faster networks.

source: Researchgate
The usage increases have many drivers. As networks get faster, more video content is pushed out, and video is the media type with the highest bandwidth requirements. As networks get faster, people can do more in the same amount of time. So in any X block of time, more data will tend to be consumed. Also, as more content, transactions and activities are available online, more people spend more time interacting online. All of that drives higher data consumption.

source: Ericsson
Perhaps significantly, Ericsson’s ConsumerLabsurveys found that 5G users consume more content than do 4G users. They stream more high-definition video, more music, play more multiplayer games, download more HD content and engage in more cloud gaming, for example. Though some might find the use of augmented reality apps at an early stage, Ericsson finds that 5G early adopters use more AR content and apps.

source: Ericsson
So 5G is “crossing the chasm,” Ericsson says. The chasm is the big jump in value proposition required for a technology product to appeal to mainstream customers.
Ericsson’s ConsumerLab research suggests that the adoption process is most advanced in South Korea, among 37 global markets where Ericsson conducted surveys.

source: Ericsson ConsumerLab
Ericsson uses segment definitions that intend to capture technology attitudes and willingness to adopt new technology.
Tech enthusiasts are high-income, well-educated, between 25 and 39 years old, power users of mobile broadband who are driven by new technology, premium devices and rich experiences. They want to be the first people to try 5G and also let the world know about it. However, they are less sensitive to any initial limitations of 5G.
The tech-intrigued are primarily younger students, heavy mobile broadband users, especially heavy on online gaming. Very interested in 5G services which offer diverse types of entertainment content.
Tech pragmatists are middle-age parents, moderate or mainstream users of mobile broadband. They often will need proof of any benefits to 5G before investing. They are interested in 5G services that support them in organizing their work and daily life.
Late tech adopters: Low-income, light users of mobile broadband who are mobile first. They have a rather basic use of online services but are interested in 5G services that enrich connecting with others.
The tech-averse are unemployed, retired, older age group and lower-income users who do not see value in 5G.
Those categories roughly map to similar adoption segments popularized by Professor Geoffrey Moore.
For most consumer technology products, the chasm gets crossed at about 10 percent household adoption. Moore does not use a household definition, but focuses on individuals. The chasm is crossed at perhaps 15 percent of persons, according to technology theorist Geoffrey Moore.

source: Medium
Both ways of counting--households for some products, persons for others--are roughly analogous, given household sizes of about 2 to 2.5. The “household versus person” correlations would not work so well in countries where household sizes are larger.
Perhaps shockingly for an innovation that promises much-faster access speeds, most respondents who plan to adopt 5G indicated that coverage was more important than speed. That would be typical for mainstream users who are less tolerant of product shortcomings.
Mainstream customers are less interested in “bleeding edge performance” and “just want it to work.” Also note that the next wave of 5G adopters is far less interested in innovative apps, unlike the “tech enthusiasts.”
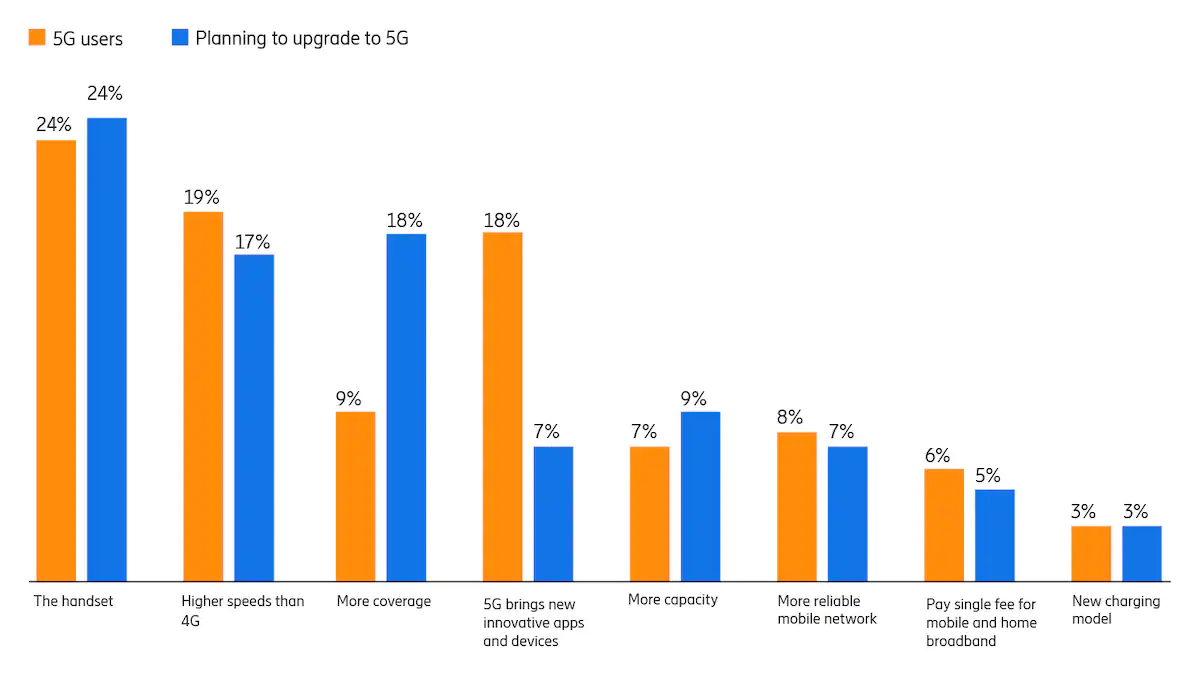
source: Ericsson
