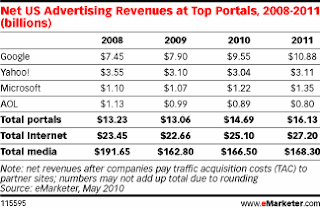
Facebook’s self-serve ad product apparently generated $300 to $400 million in revenue in 2009, a significant portion of the $800 million or so Facebook generated in total. The self-serve system allows advertisers to create small ads that appear on the right-hand side of Facebook pages and then target the ads to segments of the Facebook audience.
Friday, June 25, 2010
Facebook Is Closing the Ad Revenue Gap with the Portals
Labels:
advertising,
Facebook
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
77% of iPhone 4 Buyers Are Upgrading from Earlier Models
A survey by Piper Jaffray suggests that most early iPhone 4 buyers were upgrading from previous iPhones and that very few were switching to AT&T from other carriers. About 77 percent of iPhone 4 buyers polled in three cities (San Francisco, New York, and Minneapolis) were upgrading from old iPhones.
That's up from 56 percent last year and 38 percent in 2008, and represents brand loyalty that is likely unmatched in the mobile industry.
About 16 percent of buyers were switching to AT&T from other carriers, down from 28 percent last year.
Some 54 percent purchased the $299 32 GB model, up from 43 percent who bought the 32 GB iPhone 3GS last year.
About 28 percent of iPhone 4 buyers owned an iPad, which confirms that the people waiting in line were the most serious of the Apple fanatics. Of the 72 percent who did not own an iPad, 39 percent said they would probably buy one within the next year, while 61 percent said they would not.
About 65 percent were Mac owners, down from 75 percent at the first iPhone launch in 2007.
link
That's up from 56 percent last year and 38 percent in 2008, and represents brand loyalty that is likely unmatched in the mobile industry.
About 16 percent of buyers were switching to AT&T from other carriers, down from 28 percent last year.
Some 54 percent purchased the $299 32 GB model, up from 43 percent who bought the 32 GB iPhone 3GS last year.
About 28 percent of iPhone 4 buyers owned an iPad, which confirms that the people waiting in line were the most serious of the Apple fanatics. Of the 72 percent who did not own an iPad, 39 percent said they would probably buy one within the next year, while 61 percent said they would not.
About 65 percent were Mac owners, down from 75 percent at the first iPhone launch in 2007.
link
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
iPhone 4 Reception Issues: Use a Bumper
One of the solutions to the iPhone 4 signal reception issue is to use a rubber bumper, which was designed to protect the phone from physical damage but also keeps skin from touching the antenna, which is the cause of the signal reception problem.
Apparently the left side of the iPhone 4 receives Wi-Fi signals while the right side picks up the 3G signal for calls. And human tissue blocks reception of radio waves. Holding the device, when the antenna is on the exterior of the device, also means the antenna's physical length is affected. That's important because antenna length is proportional to the wavelength of the signals a device is trying to capture.
What seems like long ago, when people used TV antennae on their roofs to pick up broadcast TV, the antenna array was fairly large: feet worth of antennae. That was because the broadcast TV signals had a fairly long wavelength, so one needed a fairly-long antenna to catch the signals.
Cell phone signals are higher frequency, with shorter wavelength, so antennae are correspondingly shorter, measured in inches. But touching the antenna can effectively shorten its length, thus affecting reception, aside from the absorption of some of the signal.
link
Apparently the left side of the iPhone 4 receives Wi-Fi signals while the right side picks up the 3G signal for calls. And human tissue blocks reception of radio waves. Holding the device, when the antenna is on the exterior of the device, also means the antenna's physical length is affected. That's important because antenna length is proportional to the wavelength of the signals a device is trying to capture.
What seems like long ago, when people used TV antennae on their roofs to pick up broadcast TV, the antenna array was fairly large: feet worth of antennae. That was because the broadcast TV signals had a fairly long wavelength, so one needed a fairly-long antenna to catch the signals.
Cell phone signals are higher frequency, with shorter wavelength, so antennae are correspondingly shorter, measured in inches. But touching the antenna can effectively shorten its length, thus affecting reception, aside from the absorption of some of the signal.
link
Labels:
iphone 4
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
iPhone 4 Reception Problems? Stop Holding It The Wrong Way, Apple Says
Apple has acknowledged and responded to the reception problems people are having with their new iPhone 4, which seem to happen based on the way the phone is being held.
The advice? Stop holding the phone the wrong way.
The advice? Stop holding the phone the wrong way.
Apple sent Engadget the following statement: "Gripping any mobile phone will result in some attenuation of its antenna performance, with certain places being worse than others depending on the placement of the antennas. This is a fact of life for every wireless phone. If you ever experience this on your iPhone 4, avoid gripping it in the lower left corner in a way that covers both sides of the black strip in the metal band, or simply use one of many available cases."
Labels:
iphone 4
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Thursday, June 24, 2010
Marketing in a Broadband Context
You might be able to pull some nuggets from this presentation.
Labels:
marketing
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Vote: Do You Have Signal Strength Issues on Your iPhone 4?
http://polldaddy.com/poll/3387884/
And don't forget to try it using both hands, left and right. You should get different results.
And don't forget to try it using both hands, left and right. You should get different results.
Labels:
iphone 4
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gap Between Revenue and Bandwidth is The Heart of the Matter
One doesn't have to love, or even like, any of the communication providers out there to acknowledge that there is a key business problem here that directly affects any user's ability to get the most out of their communication spending and experience.
The global voice market is declining, first on the fixed line networks and now starting on the mobile networks as well. You don't have to care about that. But if you want better services, you have to acknowledge that if current revenue gets cut in half, then perhaps to a third, the people who run networks will have a hard time investing in better networks. This is not a matter of sentiment but of economics.
Everybody knows that the replacement revenues will have to come from the broadband, video, content mobile, data and commerce services realms. So the practical issue providers have is to scale the new revenues at least up to the point where voice revenue is now. Along the way service providers will have to cut costs as well, but the key issue is new revenues.
And the problem there on the bandwidth services front is that across all networks, revenue does not scale linearly with bandwidth supplied. Since nobody seems to think that can be changed too much, the burden of growth will come on the new applications and services fronts.
That means most issues related to terms of service or price of service are simply efforts to better match cost and revenue for the access part of the business. Nobody thinks the whole problem can be fixed that way, but it is part of the solution, in addition to deploying more-efficient networks and creating new services that people are comfortable paying for.
You don't have to love or like any particular service provider to hope service providers can figure this out. Unless of course you have a way of creating your own services.
The global voice market is declining, first on the fixed line networks and now starting on the mobile networks as well. You don't have to care about that. But if you want better services, you have to acknowledge that if current revenue gets cut in half, then perhaps to a third, the people who run networks will have a hard time investing in better networks. This is not a matter of sentiment but of economics.
Everybody knows that the replacement revenues will have to come from the broadband, video, content mobile, data and commerce services realms. So the practical issue providers have is to scale the new revenues at least up to the point where voice revenue is now. Along the way service providers will have to cut costs as well, but the key issue is new revenues.
And the problem there on the bandwidth services front is that across all networks, revenue does not scale linearly with bandwidth supplied. Since nobody seems to think that can be changed too much, the burden of growth will come on the new applications and services fronts.
That means most issues related to terms of service or price of service are simply efforts to better match cost and revenue for the access part of the business. Nobody thinks the whole problem can be fixed that way, but it is part of the solution, in addition to deploying more-efficient networks and creating new services that people are comfortable paying for.
You don't have to love or like any particular service provider to hope service providers can figure this out. Unless of course you have a way of creating your own services.
Labels:
business model
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
On the Use and Misuse of Principles, Theorems and Concepts
When financial commentators compile lists of "potential black swans," they misunderstand the concept. As explained by Taleb Nasim ...
-
We have all repeatedly seen comparisons of equity value of hyperscale app providers compared to the value of connectivity providers, which s...
-
It really is surprising how often a Pareto distribution--the “80/20 rule--appears in business life, or in life, generally. Basically, the...
-
One recurring issue with forecasts of multi-access edge computing is that it is easier to make predictions about cost than revenue and infra...