Chase Carey, Twenty-first Century Fox chief operating officer says a la carte TV--the ability to buy any single programming network, a TV series or a single channel, is a “farce.”
At a high level, Carey simply is arguing that the current practice of bundling channels together provides the greatest value for consumers.
Skeptics would say that is an executive defending a business model that supports supplier revenue models and profit margins.
Others would say what also is at stake is a related practice, namely the programming contracts that require distributors to buy lesser-viewed channels in order to buy a "must have" channel. In other words, to gain the right to distribute ESPN, a service provider has to agree to carry a number of other lesser-viewed channels owned by Disney (ESPN owner) as well.
But even some who support the idea that consumers ought to be able to buy their content a la carte might agree that it is not clear every consumer would save money under such a regime.
Generally speaking, consumers content to by only a few channels might save money. But most consumers would spend less money buying a bundle of channels. Heavy users would find a la carte an expensive proposition, and clearly would be better off with the bundled channel price.
Most long-time observers might agree that the total number of viable channels would shrink drastically in an a la carte retail environment, and programming executives say consumers would pay more, for a single channel, than at present.
Some studies suggest that is the case. Other studies suggest prices for most consumers might not change much. The point is that it is unclear whether most consumer would save money on video in a shift to a la carte packaging.
Programmers say prices per channel would grow substantially, but consumer think channels will not cost much. Consumers generally estimate per-channel prices in the $2 each range, while programmers tend to believe prices will be closer to 300 percent higher, for most channels, one might argue.
If a la carte access to TV channels is a "farce," it might therefore be most true in the sense that the notion most customers would save money is profoundly wrong.
A la carte might not be a farce for buyers who really only want to watch a few channels.
And a la carte is no "farce" in a business sense, for programmers. It might be an industry-changing event.
Thursday, December 12, 2013
Is A La Carte TV a "Farce?"
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
U.K. Consumers Pay Less for Communications, Ofcom Says
In France, the United States and Italy, consumers pay 2.5 percent.
In Spain, consumers spend 3.2 percent of household income (not individual or per capita income) on communications, while in Germany consumers spend 3.4 percent.
By that metric, consumers in the United Kingdom pay less than consumers in the other nations.
To create the index, Ofcom created five household profiles, ranging from a low use household with basic needs, through to an affluent household that uses lots of communications services.
Ofcom then identified the best deals available in each country that matched the needs of these households.
The United Kingdom was either the cheapest or second cheapest in four out of five of the profiles.
While U.K. prices were consistently cheaper, not all communications services were the most competitive relative to other countries.
Some caveats are in order. A different report notes that U.K. household spending on telecom grew 27 percent between 2002 and 2011, but on an inflation-adjusted basis fell two percent over that period.
So it is not clear that real prices and current prices are completely aligned.
Nor do the indices incorporate changes in product definition or quality. In 2002, most people did not buy Internet access, and what most people did buy was dial-up or lower-speed broadband.
Speeds have tripled between 2009 and 2013, for example. So no matter what the absolute price, the product is qualitatively different.
The same sort of issue exists when comparing subscription TV packages, which vary, in terms of channels provided, from country to country.
Actual purchasing behavior also is important. Packages might be available, even widely available, but be purchased by relatively few consumers. Prepaid plans, though widely purchased in many markets, are relatively low-penetration products in the U.S. market, for example.
The point is that It’s always difficult to compare costs and income, revenue and spending across countries globally.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Wednesday, December 11, 2013
First Passive Infrastructure Sharing; Then Active Element Sharing, Now Shared 4G LTE Spectrum Sharing?
It has been clear for some time that ownership of mobile cell sites is not necessarily “strategic” for a mobile service provider. Carriers often lease space on towers owned by third parties, sharing those sites with rivals.
In India and some markets in Africa, mobile service providers agree to share the cost of tower facilities. Some service providers outsource actual operations of their radio networks as well.
So it isn’t unusual anymore for a group of mobile operators to agree they will share tower site passive elements.
In the latest such example, mobile carriers Cellcom Israel Ltd., Pelephone Communications Ltd., and Golan Telecom Ltd. have agreed to build and operate a shared Long Term Evolution fourth generation radio network.
Cellcom and Pelephone also signed an agreement for the sharing of passive elements of cell sites for existing networks and an Indefeasible Right of Use (IRU) agreement with Golan Telecom for Cellcom's 2G and 3G networks.
The infrastructure sharing also might save Cellcom and Partner Communications as much as $57 million a year, according to an estimate of the brokerage unit of Ramat-Gan, Israel-based Excellence Nessuah Investment House.
What might be more unusual is cooperation in obtaining spectrum for the 4G network. Though the language is open to interpretation, and the sharing deals might require regulatory approval, it also appears the consortium will attempt to acquire common 4G spectrum as well.
That would be unprecedented, if it happens.
The 4G radio network will be built and operated by a separate, newly created entity that will be equally owned by Cellcom and Pelephone. It will be overseen by a steering committee comprising representatives of all three carriers that will make the strategic decisions regarding the 4G network by majority vote.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
AT&T Essentially Will Pay its Austin Access Customers $30 a Month for the Right to Use Browsing History to Target Ads
AT&T probably is the first Internet service provider ever to agree to pay users for the value of their browsing behavior. AT&T might not be the first app provider to do so, as some might argue Google has had a limited program in place for about a year or so.
But the big deal is that AT&T, in Austin, will give gigabit access users a choice: pay $99 a month for a gigabit access connection, with no tracking, or $70 a month, when users give AT&T the right to track browsing behavior in return for a $30 a month discount on access fees.
For policy advocates and others who think users actually own their data, and should be compensated when behavioral data is used to target advertising, that essentially is what AT&T will do in Austin, Texas.
AT&T in Austin, Texas is launching it “GigaPower” all-fiber Internet access network for prices starting at $70 a month, featuring speeds of 300 Mbps downstream initially, and a boost to 1 Gbps in 2014.
That’s huge.
But the big deal is that AT&T, in Austin, will give gigabit access users a choice: pay $99 a month for a gigabit access connection, with no tracking, or $70 a month, when users give AT&T the right to track browsing behavior in return for a $30 a month discount on access fees.
For policy advocates and others who think users actually own their data, and should be compensated when behavioral data is used to target advertising, that essentially is what AT&T will do in Austin, Texas.
AT&T in Austin, Texas is launching it “GigaPower” all-fiber Internet access network for prices starting at $70 a month, featuring speeds of 300 Mbps downstream initially, and a boost to 1 Gbps in 2014.
AT&T will offer two “U-verse with GigaPower” offers. The “Premier” version will cost $70 a month, while the “Standard” plan will cost $99 a month.
You might find it odd that the premier version costs less than the standard version.
The reason is the value to AT&T of collecting use browsing history. “U-verse with GigaPower Premier offer is available with your agreement to participate in AT&T Internet Preferences,” AT&T says.
Internet Preferences allows AT&T to use customer Web browsing information, such as the search terms people enter and the Web pages customer visit, to provide relevant offers and ads to customers based on that profil, e.
That will not be a popular practice in some quarters, but some have argued that users should be compensated when ISPs or other application providers “pay users for the value of their behavior.”
In essence, that is what AT&T is doing, compensating users at $30 a month for the right to use browsing behavior to tailor advertising and other marketing offers.
As now has become a standard industry practice, potential buyers can sign up at www.att.com/gigapower. AT&T then will build first in the areas with highest indicted demand.
“Expansion plans will, in part, be influenced by the number of Austinites voting for their neighborhood at www.att.com/gigapower,” AT&T says.
It might be overlooked, but AT&T is doing what some have advocated for some time, namely compensating users for the value of their behavior online, when used to target advertising.
That’s huge.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Tuesday, December 10, 2013
Sustainability a Key Issue for Public-Private Fiber Networks
Seattle’s effort to build a high-speed Internet access network serving 12 neighborhoods, in cooperation with Gigabit Squared, has been unable to raise financing for the venture, illustrating some of the tensions and issues related to such joint ventures.
Outgoing Seattle Mayor Mike McGinn says he’s worried about Gigabit Squared’s plans, as a result.
That might be an occupational hazard for ambitious new fiber network projects, as envisioned by Los Angeles, for example.
The Los Angeles City Council has been looking at ways to provide a metro Wi-Fi network providing free service to residents, using private investment sources.
That might require investment of $3 billion to $5 billion, and one might reasonably suggest that amount cannot be raised, given the prospects of competing with AT&T, Time Warner, Verizon, Cox, and Charter Communications, all of which offer triple play services in some parts of the city.
In addition to seeking to foster creation of a new facilities-based fiber to the home reaching every home and business in Los Angeles, the plan also envisions wholesale access requirements as well.
That would strike many observers as an unrealistic set of expectations.
The network would be required to offer free access at rates between 2 Mbps and 5 Mbps, but would be allowed to offer paid service at speeds up to a gigabit per second.
Sustainability is an issue for virtually all of the proposed joint venture networks between municipalities and private service providers.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
We Forget that Transition to Optical Fiber Once Was a Management Issue
Telecom and cable TV industry veterans with long memories will attest that the switch from copper to optical fiber in the outside plant was not pain free.
Cable TV technicians widely were troubled by the transition to hybrid fiber coax, in large part because of fear that the new technology would require new skills or new people.
So the threat of job loss, a diminution of the skills base or inability to adapt were key personnel issues.
That was true in the telecom industry as well. As Robert Mudge, Verizon president of consumer and mass business markets, recalls the issue, “employees not involved in FiOS were resisting the change.”
Confusion and apprehension were widespread, he notes.
“Some of them feared that as the company pivoted toward FiOS, it would neglect customers on its old network.
“People on the core side were saying, 'Tell me where I end up in three or four years. Where do I end up on the FiOS side?'"
Executives and managers at other firms making the transition to optical fiber in the outside plant likely can offer similar stories. The key point is that big changes will face resistance from within the organization trying to make the change.
There are other key changes in the outside plant realm as well.
As Lowell McAdam, Verizon Communications Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, recently noted, Verizon has over the last decade or so seen its operation of the industry’s latest network as a competitive advantage. FiOS unquestionably was viewed that way, initially.
But that doesn’t mean even Verizon believes fiber to the home is viable financially, everywhere, even when “our goal is to keep the network ahead of our competition.”
What Verizon is doing in Pennsylvania provides an example, where Verizon is supplying Internet access comparable to digital subscriber line using its mobile network, rather than rebuilding copper drops, even if Verizon thinks copper drops are “antiquated” and ideally would disappear.
It takes little insight to point out that the business case for FiOS-driven revenue growth, compared to the business case for revenue growth from mobile services, has changed since the 1990s.
In a nutshell, the risk-reward case for additional Verizon fiber to home deployments has gotten worse, instead of better. That doesn’t mean other contestants have similar risk-reward situations.
For independent ISPs such as Google Fiber, there are advantages beyond the direct revenue upside, primarily causing other ISPs to accelerate investments in faster broadband, and changing the prevailing pricing structure of high speed access.
For independent fixed network providers, moving as much as possible to fiber to the home is a survival issue, as the fixed network revenue model moves to high speed Internet access.
But Verizon has to weigh the use of capital in fixed compared to mobile assets. And Verizon believes the strategic and financial return from investments in mobile is higher than from further investments in FiOS.
For different reasons, the switch from legacy copper to fiber to the home continues to pose organizational challenges. These days, decisions have to be made about where to deploy "revenue growth" capital.
In many cases, the answer is "in the mobile network."
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Why Economics Matters for the Supply of Broadband Services
Frustration with the pace and scale of faster broadband in the United States is a persistent theme in some quarters. The criticisms are not without merit, at times, in an absolute sense.
As citizens debate whether an injury to a citizen anywhere on the globe is really "our problem," there is an inevitable tension between the position that "we are morally responsible to fight evil, injustice an oppression anywhere on the planet" and the position that "we just can't be everywhere and do everything."
In principle, we must balance the principle that every human being, anywhere, has exquisite value, an almost infinite obligation, with the reality that resources and will are finite.
 Often, the claim is made that U.S. Internet access "speeds are slow and costs are high," in a sort of an unhistorical sense, comparing absolute prices and speeds with those in other nations.
Often, the claim is made that U.S. Internet access "speeds are slow and costs are high," in a sort of an unhistorical sense, comparing absolute prices and speeds with those in other nations.
It always has been the case that the United States ranks something between 12th and 15th on nearly any index of "teledensity." That was true even at the peak of fixed network telephone demand, and likely will continue to be true for any measure of mobile adoption or broadband adoption as well.
The reasons are rather mundane. The countries with the fastest broadband access are smaller countries with high population density. That has direct implications for the cost of fixed networks.
Rarely, if ever, can a continent-sized country appear at the very top of indexes of Internet access speed or fixed network services. The reason is that networks are expensive when population density is low and surface area is large.
Also, in a continent-sized country, it matters whether population is clustered "around the edges," as in Canada and Australia, or distributed more widely across the interior.
Even some observers relatively critical of U.S. lagging in the pursuit of faster and ubiquitous broadband note the problem.
"We have a funny demographic: we’re not as densely populated as the Netherlands or South Korea (both famous for blazingly fast Internet service), nor as concentrated as Canada and Australia, where it’s feasible to spend a lot of money getting service to the few remote users outside major population centers," says Andy Oram of O'Reilly Radar. "There’s no easy way to reach everybody in the US."
There other unavoidable issues as well. Average costs in some countries are much higher than in others. So where housing, transportation and all other costs are higher, broadband prices also will be higher, in part because network construction costs are higher, and retail prices must be set at levels that recover the investment.
What matters in such cases is the percentage of a user's income, or a household's income, that is required to purchase high-speed Internet access, not necessarily the absolute cost. On such scores, U.S. broadband is among the most affordable in the world.
To be sure, "speed" remains an issue, but as a historical matter, Internet speeds have doubled about every four to five years.
From 2000 to 2012, the typical purchased access connection grew by about two to three orders of magnitude in about a decade.
Gigabit access availability grew 300 percent between 2010 and 2012, for example. That means gigabit access will be available in the United States, widely, between 2020 and 2023.
That requires nothing other than extrapolation from historical trends in the Internet access business.
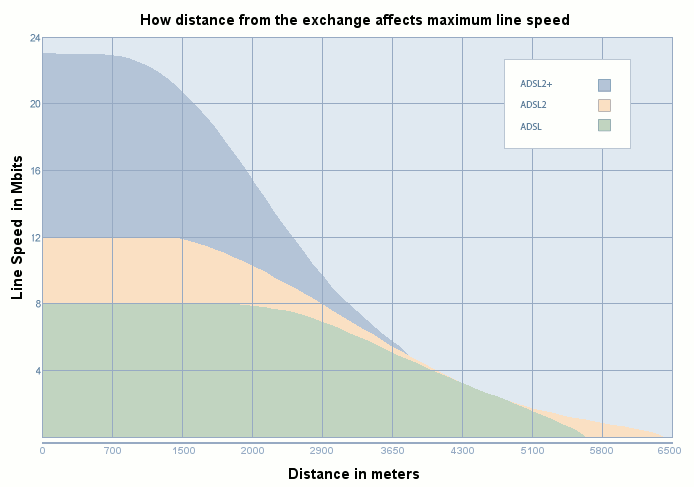
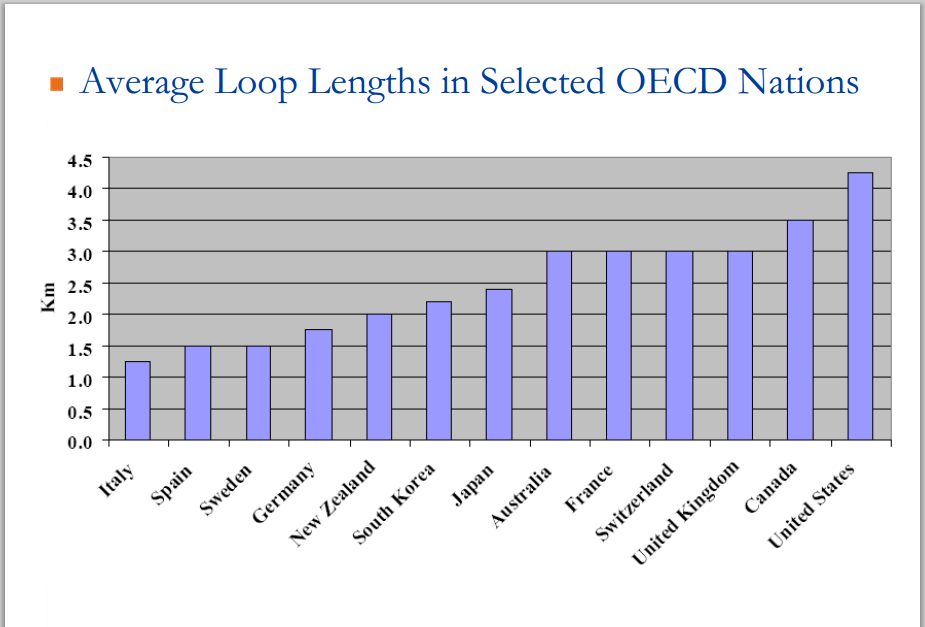
But network economics still matters. Long loop length raises cost, and the United States has significantly longer loop lengths than is typical.
The "average" loop length in the United States is about 4.25 kilofeet, meaning half are longer than 4.25 kilofeet. Lots of long loops mean lots of lines that are not capable of speeds much faster than a few megabits per second, on all-copper loops.
In most European countries, for example, loop lengths average 1.5 kft to 3 kft.
As citizens debate whether an injury to a citizen anywhere on the globe is really "our problem," there is an inevitable tension between the position that "we are morally responsible to fight evil, injustice an oppression anywhere on the planet" and the position that "we just can't be everywhere and do everything."
In principle, we must balance the principle that every human being, anywhere, has exquisite value, an almost infinite obligation, with the reality that resources and will are finite.
It always has been the case that the United States ranks something between 12th and 15th on nearly any index of "teledensity." That was true even at the peak of fixed network telephone demand, and likely will continue to be true for any measure of mobile adoption or broadband adoption as well.
The reasons are rather mundane. The countries with the fastest broadband access are smaller countries with high population density. That has direct implications for the cost of fixed networks.
Rarely, if ever, can a continent-sized country appear at the very top of indexes of Internet access speed or fixed network services. The reason is that networks are expensive when population density is low and surface area is large.
Also, in a continent-sized country, it matters whether population is clustered "around the edges," as in Canada and Australia, or distributed more widely across the interior.
Even some observers relatively critical of U.S. lagging in the pursuit of faster and ubiquitous broadband note the problem.
"We have a funny demographic: we’re not as densely populated as the Netherlands or South Korea (both famous for blazingly fast Internet service), nor as concentrated as Canada and Australia, where it’s feasible to spend a lot of money getting service to the few remote users outside major population centers," says Andy Oram of O'Reilly Radar. "There’s no easy way to reach everybody in the US."
There other unavoidable issues as well. Average costs in some countries are much higher than in others. So where housing, transportation and all other costs are higher, broadband prices also will be higher, in part because network construction costs are higher, and retail prices must be set at levels that recover the investment.
What matters in such cases is the percentage of a user's income, or a household's income, that is required to purchase high-speed Internet access, not necessarily the absolute cost. On such scores, U.S. broadband is among the most affordable in the world.
To be sure, "speed" remains an issue, but as a historical matter, Internet speeds have doubled about every four to five years.
From 2000 to 2012, the typical purchased access connection grew by about two to three orders of magnitude in about a decade.
Gigabit access availability grew 300 percent between 2010 and 2012, for example. That means gigabit access will be available in the United States, widely, between 2020 and 2023.
That requires nothing other than extrapolation from historical trends in the Internet access business.
But network economics still matters. Long loop length raises cost, and the United States has significantly longer loop lengths than is typical.
The "average" loop length in the United States is about 4.25 kilofeet, meaning half are longer than 4.25 kilofeet. Lots of long loops mean lots of lines that are not capable of speeds much faster than a few megabits per second, on all-copper loops.
In most European countries, for example, loop lengths average 1.5 kft to 3 kft.
That will start to fade, as a limitation, as more networks are reinforced with optical fiber. Newer versions of digital subscriber line technology really do help, but loop length has to be controlled.
 Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Gary Kim was cited as a global "Power Mobile Influencer" by Forbes, ranked second in the world for coverage of the mobile business, and as a "top 10" telecom analyst. He is a member of Mensa, the international organization for people with IQs in the top two percent.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
On the Use and Misuse of Principles, Theorems and Concepts
When financial commentators compile lists of "potential black swans," they misunderstand the concept. As explained by Taleb Nasim ...
-
We have all repeatedly seen comparisons of equity value of hyperscale app providers compared to the value of connectivity providers, which s...
-
It really is surprising how often a Pareto distribution--the “80/20 rule--appears in business life, or in life, generally. Basically, the...
-
One recurring issue with forecasts of multi-access edge computing is that it is easier to make predictions about cost than revenue and infra...