There is growing consensus that 5G could well mark a fundamental turning point in telecom industry history. If matters develop as hoped, a huge new wave of revenue growth, apps and services will be enabled.
And the biggest change of all is that the growth will come because computing actually becomes pervasive or ubiquitous, precisely as futurists have been predicting would eventually happen.
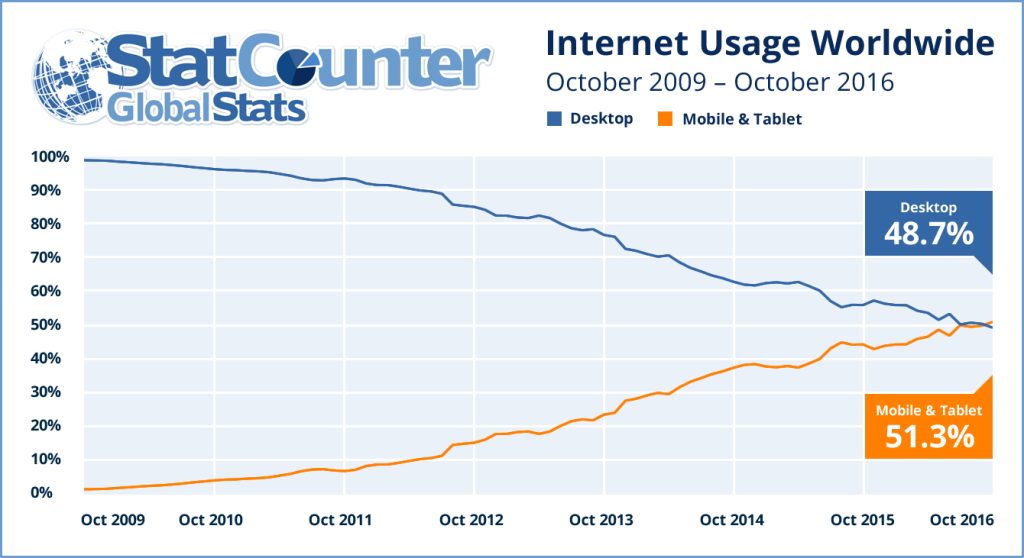
But 5G might also mark a historic change in industry dynamics for other reasons, perhaps not so welcome. It already is possible to argue that mobile data revenues and profits will follow the same path as earlier mobile services, such as voice and text messaging.
That is to say, gross revenue eventually will peak, while profit margins contract. If that happens with 4G, and if 5G represents only “more of the same,” clear problems could develop.
The biggest problem is that mobile data increasingly features a market requirement for supplying faster speeds and greater consumption, with incremental revenues that lag the increased supply.
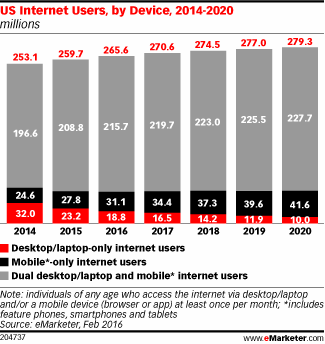
For decades now, we have seen that average revenue per megabyte or gigabyte has fallen, dramatically. That will not change in the 5G era. Not a problem, some might argue. We will simply sell more units. Up to a point, that argument has merit.
It is the same argument suppliers have used in the voice business, and in the capacity business. It works for a while. Eventually, though, the revenue per unit sold does not compensate for the fact that consumers simply require fewer units. In other cases, usage quotas rise, while prices remain flat.
In the voice business, that shows up as declining minutes of use, declining numbers of fixed network subscriptions and declining prices per unit as well. In the capacity business, that shows up as higher usage allotments or higher speeds, at the same or lower prices.
And if that problem shows up in the 4G business, it arguably will get worse in the 5G era, in part because 5G is a more expensive network, and in part because the incremental new revenues do not justify the incremental new cost.
In other words, t is conceivable 5G actually will mark the end of a profitable business model for many mobile operators whose only real option is “access” services.
The problem is that we already can foresee a time when all current revenue streams (voice, text mesaging, mobile internet access) have past their peak, in terms of users, accounts and revenue generation. 5G is not automatically going to fix that.
For many mobile operators,, 5G will be a more-expensive platform that helps supply much-higher data consumption for human users, but at rates that lag unit growth. And though new revenue opportunities should develop in the area of machine communications, much of the upside will be reaped by platform, app, device or system suppliers, not connectivity suppliers.
So 5G is not just “the next generation of mobile.” It might be a generation of mobile that sees much of the industry disappear.